Caudate nucleus: characteristics, functions and disorders
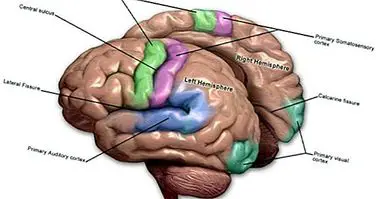
When we think about the brain, we usually imagine the superficial and outer layer, the cerebral cortex. However, below this we can find a large number of structures of fundamental importance for the survival of the human being, all participating in different types of functions such as the integration of information.
One of these subcortical structures is the caudate nucleus, whose characteristics we will see next .
- Related article: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
What is the caudate nucleus?
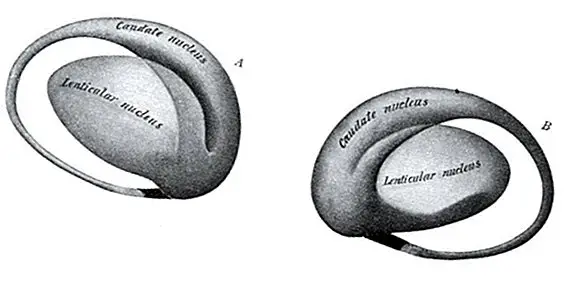
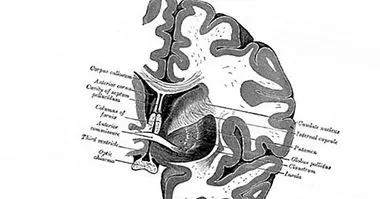
The caudate nucleus is a subcortical structure, that is, located inside the encephalon, which part of the basal ganglia . Together with the putamen and the nucleus accumbens, it forms the body known as the striated body, an element very closely linked to the control of movement.
Located above the thalamus and below the orbitofrontal cortex to subsequently bend towards the occipital lobe, the caudate nucleus connects with the rest of the basal ganglia as well as the frontal cortex and the limbic system. We have two units of this nucleus, each one of them located in a cerebral hemisphere. At the level of neurotransmitters, the caudate nucleus is mainly influenced by dopamine and GABA.
The caudate nucleus is usually divided into three parts , the head, the body and the tail. While the first is one of the thickest parts and is in more contact with the frontal cortex, the tail is connected to the limbic system. Head and body are in close contact with the lateral ventricles.
- You may be interested: "Basal ganglia: anatomy and functions"

Main functions of the caudate nucleus
The caudate nucleus and the set of basal ganglia have a high importance in the human nervous system, participating in essential functions to ensure both a correct adaptation to the environment and the survival itself by allowing the regulation of behavior through aspects such as memory and the motivation. In addition, they have also been linked to a large extent realization and coordination of movements .
Below you can find detailed some of the functions that have been attributed to the caudate nucleus.
Movement control
Together with the rest of the basal ganglia, it has traditionally been considered that the caudate nucleus has a high participation in motor control and coordination . The maintenance of the position of the members of the body, and the precision in the fine movement are some of the aspects in which the caudate participates. This can be seen in the consequences of its dysfunction, in disorders such as Parkinson's and Huntington's disease.
Memory and learning
Learning and memory are elements in which it has been found that the caudate nucleus also has an important role. For example, Procedural learning depends on this brain area . Specifically, the caudate nucleus allows the organism to be able to obtain feedback from the outside world regarding what happens and what is done. It also participates in the understanding of auditory stimuli, such as those of language.
Alarm sensation
Another of the main functions of this brain region is the perception of the alarm sensation , thanks to which we can identify that something is not working correctly and respond accordingly.
Motivation
The caudate nucleus is of paramount importance in terms of the motivation of the human being. It is a structure that connects the limbic system with the frontal cortex , so that cognitive information is transformed and linked to an emotional meaning. Its destruction can generate the appearance of extreme abulia and PAP syndrome.
Disorders and alterations in which he participates
The caudate nucleus and in general the basal ganglia as a whole, due to its multiple connections with other cerebral areas such as the orbitofrontal cortex or the limbic system, are structures of great importance for the correct functioning of the nervous system and for our adaptation to the environment. .
The presence of alterations can generate or participate in the genesis or maintenance of various types of disorder. Some of the disorders in which the caudate nucleus participates They are the following.
1. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder and Other Obsessive Disorders
As we have mentioned, the caudate nucleus has an important participation in the response mechanism to a specific situation, as well as in the sensation of alarm. In the TOC said mechanism presents an over-activation , finding that patients with this disorder usually have a high neural activation in the caudate.
In addition to OCD itself, in other disorders of a similar nature such as accumulation disorder, excoriation disorder or trichotillomania, this high level of activity can also be found.
2. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
ADHD is another disorder in which the caudate nucleus has a certain level of involvement. Specifically, in this case there is an activation below the usual, with which the ability to remember, feedback and motivation are reduced .
- Related article: "Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), also in adults"
3. Huntington's Korea
In Huntington's Korea, the caudate nucleus is one of the first areas to present neuronal death, and in the long run it ends up generating a progressive loss of executive and memory functions and the realization of uncontrolled movements in the form of twists and turns of body parts similar to a dance.
4. Parkinson
Parkinson's is another disease linked to the caudate nucleus. Specifically, parkinsonian symptoms are caused by degradation and death of the neurons that form the nigrostriatal pathway .
5. Syndrome of loss of psychic self-activation
Damage to the caudate nucleus causes the loss of motivation and hinders the connection between emotion and cognition. That is why its destruction generates a deep sense of indifference Whatever happens, even if it threatens your own survival.
6. Hypermnesia
Although it is generally not considered a disorder, the presence of hypermnesia in some people has been linked, among other brain regions, with the caudate nucleus. Specifically, it has been observed that people with above-average memory abilities They have a larger caudate nucleus than most people.
Bibliographic references:
- Carlson, N.R. (2014). Physiology of Behavior (11th Edition). Madrid: Pearson Education.
- Kandel, E.R .; Schwartz, J.H. & Jessell, T.M. (2001). Principles of neuroscience. Fourth edition. McGraw-Hill Interamericana. Madrid.
- Melnick, M.E. (2013). Basal ganglia disorders. In: Umphred DA, Burton GU, Lazaro RT, Roller ML, eds. Umphred's Neurological Rehabilitation. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Mosby; chap 20
- Packard, M.G. & Knowlton, B.J. (2002). Learning and functions of the memory of the basal ganglia. Annu Rev Neurosci 25: 563-59.