Cortical atrophy: symptoms, causes and associated disorders
There are a large number of conditions and pathologies that can cause the degeneration and death of the neurons that make up the different brain structures. When this degeneration affects the cerebral cortex it's known as cortical atrophy .
Throughout this article we will review the main characteristics of cortical atrophy. In the same way we will review the causes and diseases that cause it, its symptoms and what brain structures are involved.
- Related article: "The 15 most frequent neurological disorders"
What is cortical atrophy?
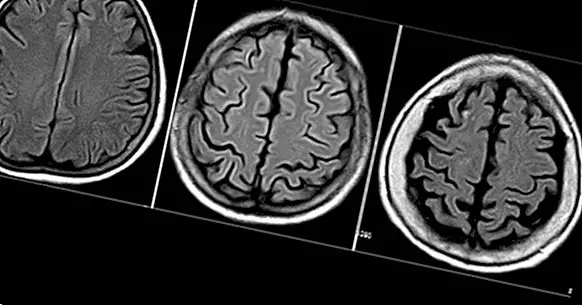
Cortical atrophy refers to the process of gradual degeneration or degradation of the cerebral cortex whose origin is found in the decrease or decrease of the neuronal population what makes it up
The concept of atrophy has its origin in Latin and its translation refers to a lack of nutrition. In the same way, the etymological foundation of the cortical word also comes from Latin and is used to refer to everything related to the cerebral cortex.
If we take into account the origins of both concepts, it is easier to deduce that cortical atrophy consists of the gradual destruction of the neuronal cells that make up the upper areas of the brain , specifically those structures that are found in the cerebral cortex, due in large part to a decline or loss of the administration of oxygen and nutrients to these areas.
What are the causes?
Due to the large number of conditions that can cause degeneration of the upper brain structures, cortical atrophy is one of the most investigated types of conditions. Among these causes are a wide variety of neurodegenerative diseases , such as Alzheimer's disease, whose main effect is the destruction of neurons and, as a consequence, the loss of brain mass.
However, there are other causes or risk factors that may favor the development of cortical atrophy. Among them are the consumption of alcohol in large doses whose toxicity causes neuronal death, as well as some infections like HIV or lack of blood supply due to cerebrovascular or ischemic strokes.
- Maybe you're interested: "Neurodegenerative diseases: types, symptoms and treatments"
What symptoms does it present?
Cortical atrophy, as well as the diseases that cause it, is characterized by causing a large number of cognitive symptoms in the person suffering from it. These changes and alterations in cognitive functions are due to the fact that these are managed by these specialized brain areas.
Cognitive functions refer to all those activities and brain processes that make it possible for people to receive, select, collect, save, transform, elaborate and rescue all the information that comes to us from the environment that does not involve it. Thanks to them, we are able to understand our environment and interact with it.
Taking into account that neuronal degeneration involves a series of alterations in these functions, the main symptoms of this include:
- Problems in memory processes.
- Language alteration .
- Loss of orientation ability
- Alterations in attention and concentration processes.
- Problems in executive functions .
- When neurodegeneration affects the frontal lobe, it can cause behavioral and personality disorders.
However, this symptomatology may vary according to the neurodegenerative disease that causes it; being able to vary both the intensity and the amount of symptoms characteristic of each clinical picture.
What brain regions does it affect?
As already mentioned throughout the article, cortical atrophy consists of the degeneration of neurons in the cerebral cortex. Therefore, it will exert its effects in all the structures that are in it.
These structures are divided into the different large areas that make up the cerebral lobes . They are the following.
1. Frontal lobe
Located in the anterior area of the brain, the lobe is the most recent of the cerebral lobes at the phylogenetic level. This means that it is only found in vertebrate species and especially more developed in complex species such as hominids.
Among its main functions are those of develop and control behavior, as well as linguistic production and abstract thinking . Therefore, all those neurodegenerative diseases that affect this area can seriously compromise the correct functioning of these brain tasks.
- Related article: "What is the frontal lobe and how does it work?"
2. Parietal lobe
The parietal lobes are located in the upper area of the skull.The neuronal atrophy of this region causes serious alterations in the ability to integrate sensory information , as well as to understand it and give it a meaning.
3. Occipital lobe
This third lobe is located in the posterior area of the brain. In addition, it is the main one in charge of receiving and transmitting the visual information that comes from the rest of the visual structures.
4. Temporal lobe
Finally, the temporal lobe is located in the lower area of the brain. Any type of injury or atrophy in this region usually causes the most characteristic symptoms of neurodegenerative diseases, since they are all those related to the processes of memory and thought .
With what diseases does it relate?
Although there are many other causes, such as alcoholism or ischemic accidents, which can cause the degeneration and destruction of neurons in the cerebral cortex; The main causes of this atrophy are neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Pick's disease or Lewy body dementia.
1. Alzheimer's disease
Senile dementia of Alzheimer's type consists of a condition of neurodegenerative nature in which the person experience an alteration of memory processes , as well as other mental abilities, manifested through cognitive and behavioral symptoms.
- Related article: "Alzheimer's: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention"
2. Pick's disease
Pick's disease is a strange dementia similar to Alzheimer's caused by an accumulation of Pick's bodies in brain neurons. The main symptoms are related to behavior disorders such as compulsive and repetitive behaviors, or emotional disturbances such as sudden changes in mood and a loss in the expression of emotions .
3. Dementia due to Lewy bodies
This last type of neurodegenerative disease shares a large number of symptoms with other conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. However, despite having motor, behavioral and memory symptoms characteristic of these dementias, in Lewy body dementia the patient experiences a fluctuation in the intensity of the symptoms accompanied by highly realistic visual hallucinations .
- Maybe you're interested: "Dementia with Lewy bodies: symptoms, causes and relationship with Alzheimer's"
Differences with posterior cortical atrophy
Unlike the cortical atrophy referred to throughout the article, posterior cortical atrophy has a much earlier onset age , the first symptoms can appear between 50 and 60 years.
In addition, this neurodegenerative condition it is distinguished by especially presenting visual symptoms . These symptoms include an alteration in the ability to understand the environment that surrounds the person, as well as problems when perceiving precise and specific objects that they find in the patient's visual field. For example, the person is completely unable to see or find the keys that are in front of her.
With the development of posterior cortical atrophy, the person begins to experience behavioral and cognitive symptoms typical of other atrophies, but with the added disadvantage that they suffer at much younger ages.