Cortisol: the hormone that generates stress
Much is talked about in recent times of stress , a phenomenon known as "the epidemic of the 21st century". The rhythm of life that we lead, the socioeconomic situation and the working conditions to which we are subjected contribute remarkably to the appearance of this condition.
Cortisol is one of the hormones associated with stress along with adrenaline, and its main function to prepare the body for the moments of greatest activation in which it is necessary to be alert. Stress is an adaptive response that prepares our body to carry out a fight or flight response to a dangerous or threatening stimulus. However, when this phenomenon occurs daily and becomes chronic, the pathological stress that causes serious problems for physical and mental health appears.
- Related article: "Chronic stress: causes, symptoms and treatment"
What is cortisol
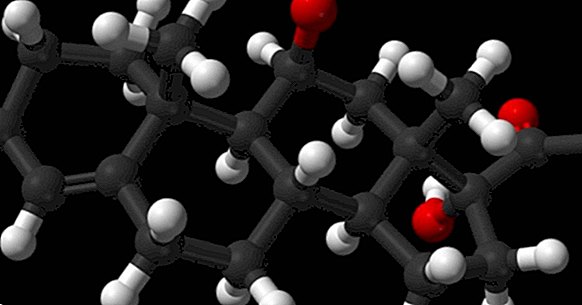
Cortisol, also known as hydrocortisone, is a glucocorticoid . It is produced on top of the kidneys, in an area known as the adrenal cortex, in response to stress (physical or emotional), and its synthesis and release is controlled by the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and its circadian rhythm.
In the morning, the amount of cortisol rises until reaching its peak around 8:00 a.m. (taking into account a normalized sleep schedule), due to the need to generate energy sources after a long night. In the afternoon it also increases to keep us active, but then it descends progressively.
Stress hormones: cortisol and adrenaline
Cortisol and adrenaline they are two related hormones with stress but they have different functions. Understanding the function of each of these chemicals can help us understand what happens in our body when we are faced with a stressful stimulus. The reaction to stress is an instinctive behavior that has allowed the survival and development of human beings, since our body is programmed to act in situations of emergency or danger.
However, this thing that has worked so well throughout history, creates serious problems today because of the way we humans live. Also, this phenomenon is not only produced by physical stimulation, but our thoughts can also cause stress (for example, when a person suffers a post-traumatic stress situation and constantly relives a stressful situation of the past), which can lead us to a situation of physical and mental exhaustion excessive.
How adrenaline works
In the face of a stressful stimulus, adrenaline it gives us a quick boost , so that our energy increases and so we can escape from danger. The breathing, pulse and heart rate are accelerated so that the muscles respond more quickly. The pupils dilate, the blood circulates at a higher speed and it moves away from the digestive system to avoid vomiting. In general, the whole body is prepared to react quickly to certain stimuli, so that you do not act at too slow rates.
These physiological functions of adrenaline are complemented by other psychological functions such as keeping us alert and being more sensitive to any stimulus. Adrenaline, besides being a hormone, is also a neurotransmitter that acts in the brain. In this way, an intense dialogue is established between the nervous system and the rest of the organism, which is very useful when it is necessary to trigger processes that affect many areas of the body in a short time.
What role do you have in alarm situations?
In situations of stress, the level of cortisol also increases. Its main functions are increase the amount of sugar in the blood , and also suppress the immune system to save energy and help the metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates. This can be very appropriate for a specific moment, but not when the stressful situation is part of our day to day.
The release of sugar in the blood has the function of maintaining an appropriate level of energy to respond effectively to the stress situation and allows us to be alert. In fact, it is the adrenaline of the brain that sends the signal for glucose to be released into the bloodstream (what is known as blood sugar), but cortisol contributes to its synthesis. It also contributes to the use of fats and proteins as energy substrates.
As we have seen, another response of cortisol to a stressful situation is that It inhibits the immune system , because all the energy is necessary to control stress.In addition, this hormone also causes an increase in histamine, which explains why people tend to get sicker or suffer from herpes or allergies when they suffer from this phenomenon.
Relationship with stress
The excess of cortisol that derives from remaining in stressful situations in a prolonged way causes certain imbalances due to the waste of energy that we are experiencing . Some of the symptoms that we can suffer are the following:
- Sensation of fatigue, fatigue and exhaustion.
- Problems of memory, concentration and learning.
- Predominance of irritability, anger and aggression.
- Physical pain (for example, head or stomach)
- Weakening of the immune system and, therefore, diseases, allergies, etc.
When stress manifests for a long time, then it is possible to experience complex pictures of anxiety, feelings of failure, insomnia or depression.
Other consequences of the excess of this hormone
Although cortisol has a bad reputation because it is associated with something as negative as chronic stress or burnout, in the human organism it performs a great number of vital functions. Among other things, it allows our rhythms to adapt to the rhythm demanded by certain situations, such as the moments when our physical integrity may be in danger or when a test is approaching which we must overcome. Although the sensation is not always pleasant, that does not mean that it is not necessary or practical.
However, in the long term it causes a series of unwanted effects. For example, the production of cortisol, either by deficit or excess, can interfere with the production of thyroid hormones and the conversion of these from T4 to T3.
Cortisol interrupts the reproductive system, causing infertility or even miscarriage when cortisol levels are too high or chronically elevated. In addition, the chronic increase in cortisol can cause intense hunger and food cravings due to the metabolic disorder that occurs, and also influences mental blocks and memory problems related to the feeling of "staying blank."
conclusion
Cortisol is a hormone related to stress that in itself is not negative . However, when stress becomes chronic and becomes pathological, it can create a series of problems or negative consequences for the person. Among these consequences are:
- Decreased defenses
- Stomach problems, diarrhea or constipation
- Appetite problems
- Humor changes
- Difficulty concentrating and memory problems
- Fatigue and fatigue
- Headaches
- Hypertension
- Infertility and interruption of menstruation
If you are going through a stress situation and want to know what you should do, in this article: "10 essential tips to reduce stress" you can find some keys to combat it.