Differences between mitosis and meiosis
The human body is made up of 37 trillion cells. It is surprising that this immense quantity originates in a single cell that is conceived during fertilization. This is possible because of the ability of cells to reproduce themselves, a process that involves dividing them in two. Little by little, it is possible to reach the aforementioned amount, forming the different organs and cell types.
Now, there are two basic mechanisms by which cells can get to reproduce: mitosis and meiosis. We'll see now the differences between mitosis and meiosis and their characteristics .
- Maybe you're interested: "Genetics and behavior: do genes decide how we act?"
Mitosis and meiosis
We have seen that little by little, a few cells can give rise to an entire organism, be it a human being or an immense whale. In the case of the human being, it's about diploid eukaryotic cells , that is, they present one pair per chromosome.
The structure of the chromosome is the most compact and condensed form that DNA can present along with structural proteins. The human genome is made up of 23 pairs of chromosomes (23x2). This is an important data to know one of the main differences between mitosis and meiosis, the two classes of cell division that exist.
The eukaryotic cell cycle
The cells follow a series of patterns sequentially for their division. This sequence is called the cell cycle, and consists of the development of four coordinated processes: cell growth, DNA replication, duplicate chromosome distribution and cell division . This cycle differs in some points between prokaryotic (bacteria) or eukaryotic cells, and even within eukaryotes there are differences, for example between plant and animal cells.
The cell cycle in eukaryotes is divided into four stages: phase G1, phase S, phase G2 (all of them are grouped in the interface), phase G0 and phase M (Mitosis or Meiosis).
1. Interface
This group of stages has as its purpose prepare the cell for its imminent partition in two , following the following phases:
- Phase G1 (Gap1) : corresponds to the interval (gap) between a successful division and the beginning of the replication of the genetic content. During this phase, the cell is in constant growth.
- Phase S (Synthesis) : it is when DNA replication occurs, ending with an identical duplicate of the genetic content. In addition, chromosomes are formed with the most known silhouette (in the form of X).
- Phase G2 (Gap2) : cell growth continues, in addition to the synthesis of structural proteins that will be used during cell division.
Throughout the interface, there are several checkpoints to verify that the process is being carried out correctly and that there is no error (for example, that there is no bad duplication). In case of any problem, the process stops and an attempt is made to find a solution, since cell division is a vitally important process; Everything has to go well.
2. Phase G0
Cell proliferation is lost when the cells are specialized so that the growth of the organism is not infinite. This is possible because the cells enter a resting phase called the G0 phase, where they remain metabolically active but do not present either cell growth or replication of the genetic content, that is, they do not continue in the cell cycle.
3. Phase M
In this phase it is properly when the partition of the cell occurs and mitosis or meiosis develops well .
Differences between mitosis and meiosis
In the phase of division is when either mitosis or meiosis occurs.
Mitosis
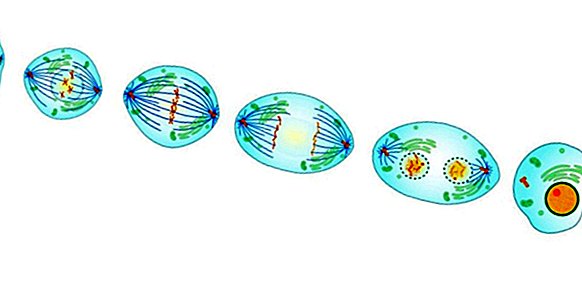
It is the typical cell division of a cell giving rise to two copies . As with the cycle, mitosis has also traditionally been divided into different stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Although for a simpler understanding, I will describe the process in a general way and not for each phase.
At the beginning of mitosis, the genetic content is condensed in the 23 pairs of chromosomes that make up the human genome. At this time, the chromosomes are duplicated and form the typical X-image of the chromosomes (each side is a copy), joined in half through a protein structure known as a centromere. The nuclear membrane that encloses the DNA is degraded so that the genetic content is accessible.
During the G2 phase, different structural proteins have been synthesized, some of them doubled. They are called centrosomes , which are each placed on a pole opposite each other from the cell.
The microtubules, the protein filaments that make up the mitotic spindle and which bind to the centromere of the chromosome, are prolonged from the centrosomes. to stretch one of the copies towards one of the sides , breaking the structure in X.
Once on each side, the nuclear envelope is reformed to enclose the genetic content, while the cell membrane is strangulated to generate two cells. The result of mitosis are two sister diploid cells , since its genetic content is identical.
Meiosis
This type of cell division it only happens in the formation of the gametes , which in the case of humans are sperm and ovules, cells that are responsible for giving shape to fertilization (they are called the germ cell line). In a simple way, it can be said that meiosis is as if two consecutive mitoses were made.
During the first meiosis (meiosis 1) a process similar to that explained in mitosis occurs, except that the homologous chromosomes (the pair) can exchange fragments among them by recombination. This does not happen in mitosis, since in this they never come into direct contact, unlike what happens in meiosis. It is a mechanism that offers more variability to genetic inheritance. Further, what separates are the homologous chromosomes, and not the copies .
Another difference between mitosis and meiosis occurs with the second part (meiosis 2). After having formed two diploid cells, they are divided again immediately . Now the copies of each chromosome are separated, so the final result of the meiosis are four haploid cells, since they only present one chromosome of each (not couples), to allow that in fertilization new pairings are formed between the chromosomes of parents and enrich genetic variability.
Overall summary
In order to compile the differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans, we will say that the final result of mitosis are two identical cells with 46 chromosomes (pairs of 23), while in the case of meiosis there are four cells with 23 chromosomes each one (without partners), in addition to its genetic content can vary by recombination between homologous chromosomes.
- Maybe you're interested: "Differences between DNA and RNA"