Franz Boas: biography of this influential American anthropologist
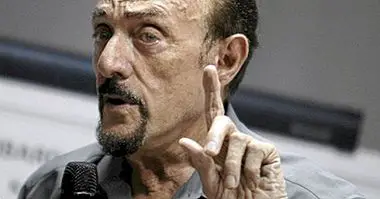
Franz Boas (1958-1942) is known as the father of American anthropology. He has also been considered one of the four fathers of anthropology, for having laid the foundations of one of its branches: cultural anthropology.
In this article we will see a biography of Franz Boas very summarized, as well as some of the main characteristics of his life and work.
- Related article: "Anthropology: what is and what is the history of this scientific discipline"
Biography of Franz Boas: life and work of this anthropologist
Franz Boas was born on July 9, 1858 in Minden, Germany. His grandparents were Jews and his parents had assimilated some of the German values of the Enlightenment era, as well as liberal ideas of the revolution of 1848.
Inevitably Franz Boas developed sensitivity to both groups, while not subscribing sharply towards any of them and was able to develop a critical consciousness towards anti-Semitism and nationalism . Likewise and from a very young age, he developed a great interest in the natural sciences, and soon after he became interested in studies in the history of culture.
Time after participating in military services, Boas studied geography in Berlin, where his interest in cultural processes grew beyond demographics. In 1886 he visited Kwakiutl and other Canadian tribes, and upon his return to the United States he was the editor of the journal Science. Later he collaborated in the preparation of the anthropological exhibitions of 1893 in the National Museum of History of Chicago, where he exhibited part of his work.
Finally he worked as a professor in different universities in the United States and as curator of anthropology at the American Museum of Natural History , in New York, where he was also director and editor of the research reports of different studies that analyzed non-western cultures and societies.
Beginnings of cultural anthropology
Like many of the pioneers of anthropology, Franz Boas began his training in mathematics, physics, which he complemented through different studies that finally allowed him to develop his main works. For example, received training in philosophy , where he was especially interested in Kant's thought. From there he came to psychophysics and soon became interested in addressing some problems of the epistemology of physics.
In other words, it worried how the knowledge that this discipline validated and spread was being constructed. Later, Franz Boas specialized in geography , field that allowed him to explore the relations between the subjective experiences and the material conditions of the world. In this context there was an important debate on whether the determining factors were physical or cultural, and Boas was closely related to other researchers who analyze this debate from the migration processes.
For its part, anthropology was developing around an evolutionary perspective of culture. This means that the studies that were developed justified the cultural differences based on biological arguments that said that some human "races" have greater or better abilities to adapt, or not, to certain contexts.
In general and in that historical context, these arguments supported racist and exclusionary practices that affect people whose skin is not white. From here and from his interest in migratory processes, Boas studied how new environments affect migrants, and not the other way around, as was suggested by some studies.
- Related article: "Differences between Psychology and Anthropology"
From cultural evolutionism to cultural relativism
One of the main contributions of Franz Boas to modern anthropology was the shift towards a relativistic perspective of culture. What was broadly proposed was that cultural differences are mediated by culture, and not so much by biology, as the evolutionary approach has been arguing.
In other words, Boas argued that the origin of the cultural difference was not given by biology , which inevitably must be taken into account to analyze the processes of racialization. From his research, Franz Boas was positioned as one of the greatest representatives of the questioning of white supremacy that went through the anthropologist's studies.
This was one of the origins of cultural anthropology, I understand that culture is the local context where human action occurs, which added to the other three branches of anthropology that were already being developed: linguistics, physics and archeology.
Finally, Boas Approaching Ethnography arguing that all cultural phenomena should be considered worthy of being studied in their specificity and particularity, which led him to establish a rupture with the cultural laws formulated by science. He developed a preference for empiricist practices, and was finally able to develop cultural relativism as an important methodological and theoretical tool, which would serve both for data collection and analysis.
- Maybe you're interested: "The main methods in psychosocial research"
Legacy and outstanding works
Franz Boas served as a teacher in Massachusetts and Chicago and founded the American Anthropological Association, as well as the American Anthropology magazine, since 1898.
Some of the most outstanding works of Franz Boas They are the following books: Race, Language and Culture (race, language and culture), 1940; Anthropology and Modern Life (Anthropology and modern life) of the year 1928; The Relation of Darwin to Anthropology (The relationship of Darwin and anthropology), text published posthumously.
Bibliographic references
- New World Encyclopedia. (2017). Franz Boas. Retrieved June 18, 2018. Available at //www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Franz_Boas.
- Tax, S. (2018). Franz Boas. German-american anthropologist. Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved June 18, 2018. Available at //www.britannica.com/biography/Franz-Boas.