High GGT: symptoms, possible causes and characteristics
It is likely that more than once we have done some blood tests, either to check the values of elements such as cholesterol, triglycerides or blood sugar or before the presentation of any kind of symptoms that makes think about the existence of a specific disease (in which case a more specific analysis is performed).
Thanks to them we can get to detect very diverse pathologies, observing for example altered levels of lipids, leukocytes or even some enzymes. An example of this occurs when we have gamma glutamyl transferase or high GGT , an indicator of the existence of possible damage to organs such as the liver. Throughout this article we will make a brief dissertation about what it is and what it may mean to have the GGT high, as well as some conditions that may cause it.
- Related article: "Types of major cells of the human body"
What is the GGT and when we start to have it high?
It is called gamma glutamyl transferase or GGT an important enzyme present in various organs of the human body , with special preponderance in the liver (being this the organ in which it is in greater proportion), the heart and the gall bladder but also being present in others like the kidneys or the brain.
This enzyme has as its main function metabolize the main antioxidant that makes our body, glutathione , as well as transferring it to other amino acids. It contributes in this way, among other things to maintain health and cellular homeostasis and to strengthen the immune system. As we have said, it is part of different organs, being able to find certain levels of said enzyme in blood.
In general, normal values between 0 and 30 or between 7 and 50 units per liter of blood are considered. Above these values is considered that this enzyme is at a high level, something that is indicating the presence of damage to any of the aforementioned organs, basically in the first three and being the most likely liver. The increase It is usually due to a filtration of the enzyme through damage or injury to these organs .
How are your levels evaluated and evaluated?
Although it is possible that in principle it does not seem to generate symptoms, it is usual that what generates high levels of GGT produces different alterations.
These can vary greatly based on the causes, but the most common are the presence of jaundice or yellowing of eyes and skin, weakness, changes in urine color and feces (the first is usually darkened and the second is clear), sudden loss of appetite, pruritus on the skin, discomfort and gastrointestinal pain or nausea and vomiting, being indicators of the presence of damage that makes recommendable the relevant analysis.
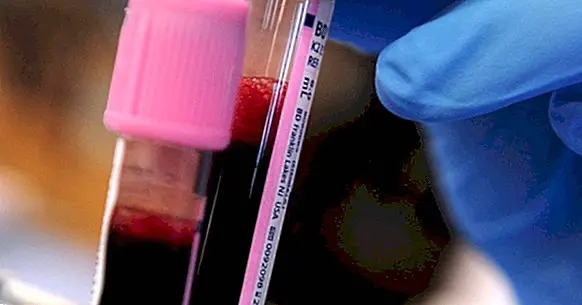
The assessment of GGT levels it will be done through a blood test , usually after a period of time without eating or drinking. It is no more dangerous than other blood tests, and once in possession of the sample the analysis is relatively quick to do.
However, despite this it should be noted that the fact of having the GGT high does not have an identifiable single cause, not serving its levels as an accurate indicator of where the damage may be. That is why it is often necessary to perform complementary analyzes that value other enzymes.
Possible causes of high GGT
As we have just commented, there are many reasons that can cause us to have high GGT, often needing to analyze the levels of other substances to determine the cause concrete of said alteration. Among the most common causes of its elevation above normal, we can highlight the following.
1. Hepatitis
The different types of hepatitis, which they are inflammations of the liver which can come from so varied causes As infection by a virus or food poisoning, have also been associated with the presence of alterations that facilitate the GGT to leak into the blood, generating an increase in their levels.
- Maybe you're interested: "Hepatitis: what it is, types, symptoms and treatments"
2. Alcoholism and alcoholic cirrhosis
The excessive consumption of alcohol and its consequences on the liver are one of the possible causes that can generate that we have a high GGT, due to the existence of lesions through which the enzyme leaves the blood flow. An example is found in alcoholic liver cirrhosis, in which the liver has degenerated in such a way that It presents a lot of scarring and a very diminished organ functioning .
3. Diabetes mellitus
Another of the conditions that can generate an elevation of GGT levels is diabetes mellitus, regardless of whether it is insulin dependent or not. The mentioned increase usually occurs mainly in those people who do not follow the treatment or the medical recommendations, being habitual in such cases that lesions in the liver can appear. Fortunately, good glycemic control prevents the GGT from increasing .
4. Cysts and liver tumors
A reason that can also cause a high level of GGT in blood is the presence of liver lesions derived from the damage caused by cysts and tumors, either because we are dealing with a tumor that appears in the organ or because, despite being somewhere else, it generates pressure or compression in / of this.
5. Drug consumption
Not always the elevation of GGT is due to a disease, but it can also be derived from the effects of the consumption of certain drugs or substances. Among them can stand out some antibiotics or drugs to treat epilepsy . Another type of drug that can generate a high GGT are oral contraceptives. In addition, substances such as alcohol or phenobarbital (a barbiturate, anxiolytic and sedative) also generate an elevation of the GGT.
6. Blocking of the vesicular channels or blood hypoperfusion
In addition to the above, there are other diseases and injuries that can cause the emission of GGT in the blood to be excessive, and the causes of this can be found in problems in the communication of the gallbladder with the liver or the absence of the arrival of enough blood in the area. It can also be caused by internal bleeding.
7. Heart failure
Especially frequent in the elderly population, the presence of cardiac problems such as heart failure also generates an elevation of the GGT, in this case not so derived from the liver but from the main organ of the cardiovascular system.
Bibliographic references:
- Chernecky, C.C. & Berger, B.J. (2013). Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGTP, gamma-glutamyltransferase) - blood. In: Chernecky CC, Berger BJ, eds. Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures. 6th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders: 559-560.
- American Accreditation HealthCare Commission (2017). Gamma-glutamyl transferase (CGT) blood test. MedlinePlus [Online]. Available at: //medlineplus.gov/english/article/003458.htm.