Lenticular nucleus: parts, functions and associated disorders
The basal ganglia are a series of parts of the brain located in the depths of the brain that are of great importance for the performance of various functions. It is a set of different structures and substructures, which can be grouped according to their connections between them.
One of these structures or rather a set of them is the so-called lenticular nucleus , which is especially relevant in the management of motor skills, as well as in learning and motivation.
- Related article: "Basal ganglia: anatomy and functions"
The lenticular core: parts and characteristics
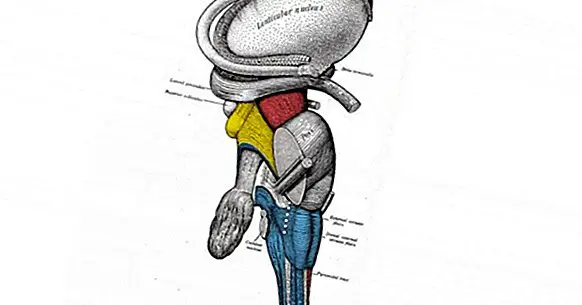
The lenticular nucleus is a subcortical structure of the brain, located in the inner part of this. This nucleus is part of the basal ganglia, a set of structures configured by gray matter (that is, it is mainly neuronal somas and dendrites).
Also called the extraventricular nucleus of the striatum , the lenticular nucleus is formed by three segments, although said three segments can be divided mainly into two structures; putamen (which would be the outermost segment) and pale globe (which would pick up the middle and inner segments).
Thus, it can be considered that the lenticular nucleus is the union of two other structures of the basal ganglia, putamen and pale balloon .
This cuneiform structure is in contact with the internal capsule, which separates it from the thalamus and the caudate, and with the external capsule that separates it from the cloister and the insula. It connects with the aforementioned thalamus, the cerebral cortex and the set of structures that make up the brainstem.
Functions associated with this subcortical structure
The lenticular nucleus, like the set of structures that make up the basal ganglia, is a structure or set of structures of great importance for the correct functioning of the human being. Specifically, it has been observed that it has great importance in the following areas.
Motor skills
One of the aspects that has been most researched and that has been known for a long time is the great importance of the lenticular nucleus in motor skills and movement management and coordination . Its main task in this sense is to adapt the movement to the situations that are being lived and to adjust to situational demands.
Posture maintenance
The lenticular nucleus participates not only in the realization of concrete movements, but also has relation with the maintenance of the posture. Damage to the lenticular core can cause gait difficulties , uncoordinated or uncontrollable tremors.
Movement automation
The automation of movements is also affected by the lenticular nucleus, by allowing habituation to be acquired in its realization.
Learning
The lenticular nucleus has influence on the learning processes . Concretely it helps to generate procedural learning. In addition, through its various connections, the lenticular nucleus contributes to the creation of categories when organizing and structuring the world.
Motivation
Like other areas such as the caudate nucleus, the lenticular nucleus also contributes greatly to link the rational with the emotional , allowing both types of information to be integrated. This means that thanks to their connections we can link a knowledge or stimulus to an emotion, which can motivate or demotivate us.
- Related article: "Are we rational or emotional beings?"
Disorders linked to the lenticular nucleus
The presence of alterations and injuries in the basal ganglia can have devastating repercussions on the health of the organism, as well as diminish its most basic capacities. Some of the alterations that are linked to damage to the lenticular nucleus are the following.
Subcortical dementias
The progressive degeneration caused by this type of dementias tends to start in different subcortical structures, being one of the most frequent the basal ganglia. The dementias produced by Parkinson's or by Huntington's Korea They are two of the best known, which occur with incoordination of the march, performing different spasmodic movements either at rest or during the performance of movements and a loss of memory and executive abilities.
Psychomotor disorders
Disorders such as tics or that of Gilles de la Tourette, or Parkinson's disease itself without it having to cause dementia, are also influenced by the alteration of the basal ganglia.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
OCD has also been linked in part with the hyperactivation of the basal ganglia, especially the caudate nucleus and the putamen (forming this latter part of the lenticular nucleus).
- Related article: "Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): what is it and how does it manifest?"
ADHD
ADHD is another of the disorders that is influenced by the presence of damage to the lenticular nucleus, making it difficult to maintain motivation and promoting the appearance of tics and agitation.
Bibliographic references:
- Carlson, N.R. (2014). Physiology of Behavior (11th Edition). Madrid: Pearson Education.
- Kandel, E.R .; Schwartz, J.H. & Jessell, T.M. (2001). Principles of neuroscience. Fourth edition. McGraw-Hill Interamericana. Madrid.