Lingual rotation: functions and characteristics of this part of the brain
There are many structures that are part of the nervous system, being the cerebral cortex one of the most developed in the human being. In it it is possible to observe the presence of a large number of convolutions and grooves, being folds that allow the condensation in a small space of a large amount of neuronal mass.
These folds are part of the gray matter of the brain and participate in different functions. One of them is the lingual turn , about which we will talk briefly throughout this article.
- Related article: "Brain twists: the 9 main folds of the brain"
The lingual turn: what is it and where is it?
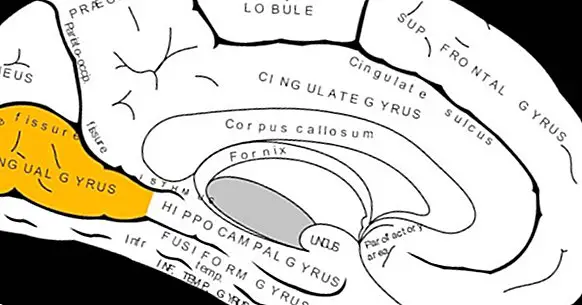
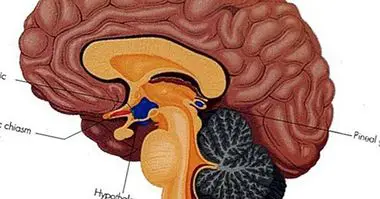
It receives the name of lingual turn one of the circumvolutions or cerebral turns, that is to say the part that leaves to the outside of the folds present in the cerebral cortex. It is a gyrus not as well known or popular as others like the supramarginal gyrus, but nevertheless it seems to have a great importance in different brain functions.
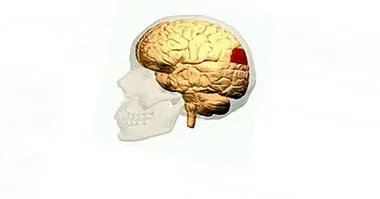
The lingual turn It is located in the occipital lobe , in its middle part, and it is located between the calcarine sulcus and the collateral sulcus. At its ends it joins on one side joins the visual area to be in contact with the wedge, while on the other it ends by joining the parahipocampal rotation in the temporal lobe.
Although the name of this brain region seems to indicate a relationship with speech, the truth is that its name has nothing to do with its function: the name of this turn comes largely from its tongue-like shape . However, curiously yes that is involved in some aspects of language, but not in the oral.
- You may be interested: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
Main functions of this part of the brain
The lingual gyrus is a brain gyrus that is involved or that participates in different functions of great relevance for the human being . Among them we can highlight the following.
1. Importance in visual processing and color perception
It has been observed that the lingual turn, as an active part of the occipital lobe, is associated with the ability to encode complex images. It also seems to be linked to the subjective perception of color, producing its achromatopsia lesion.
2. Participate in visual memory
Likewise, different researches have shown that the lingual turn not only participates in the codification of images but also has a relevant role in visual memory, Your injury causes different problems of recognition of stimuli . In fact, the lingual turn is one of the areas that allows us to identify stimuli with symbolic meaning, such as letters. In addition, it also allows you to recognize faces and objects.
3. Reading
We have said previously that the lingual turn, in spite of its name, was not associated to a large extent with the capacity of the speech but that it did have some involvement in the language. And is that another of the great functions associated with the lingual turn has to do with reading, being one of the parts of the brain that allows identify and name stimuli through vision to later transform them, being a relevant first step to allow reading.
4. Semantic processing
In addition to the merely visual, the lingual turn participates in the processing of semantic information both in situations in which the visual stimulus has symbolic elements per se or the subject tries to attribute them.
5. Involvement in emotion
The lingual turn is also connected to the parahipocampal turn , so that it is in contact with the limbic system. It has been observed that the activation of this turn correlates with the impression of emotionality to the images.
6. The ability to imagine: divergent thinking and creativity
The ability to create and develop strategies different from the usual and known in order to solve problems is also linked to the activity of the lingual turn, although it is more strongly associated with the frontal lobe. Specifically, the lingual turn would be linked to the creation and elaboration of mental images that are part of the imagination.
7. The ability to dream
Another aspect that has been associated with the lingual turn is the link that has been observed between this turn and the possibility of elaborate images during sleep , being at least partly responsible for us to have dreams.
Problems associated with your injury
The lesion of the lingual gyrus can generate different types of problems and deficits that can suppose a deterioration or limitation of the functionality of the human being in his day to day.Among them, the possible emergence of pure alexia or impossibility to read (despite retaining the ability to write).
Another problem that may appear is prosopagnosia, a type of visual agnosia in which we are not able to recognize familiar faces.
Memorization and spatial navigation are also altered , as well as achromatopsia or color blindness is possible.
It has also been observed that the lesion of the lingual gyrus, generally due to cerebral infarcts in said area, tends to generate the loss of oneiric ability (ie to have dreams). In addition to the above, the lingual turn has also been associated with other problems: an example is the recently studied link between this turn and the severity of anxious-depressive symptomatology in young people.
Also the excess activation of this area has effects: it has been observed that visual noise can be generated, the perception of small black and white points in the entire visual field that resemble the effect of snow that would happen on an old television and whose antenna malfunctioned.
Bibliographic references:
- Couvy-Duchesne, B .; Strike, L.T .; from Zubicaray, G .; McMachon, K.L .; Thompson, P.M .; Hickie, I.B .; Martin, N.G. & Wright, M.J. (2018). Lingual Gyrus Surface Area is associated with anxiety-depression severity in young adults: a genetic clustering approach. eNeuro, 5 (1).
- Bogousslavsky, J .; Miklossy, J .; Deruaz, J.P .; Assal, G. & Regli, F. (1987). Lingual and fusiform gyri in visual processing: a clinico-pathologic study of superior altitudinal hemianopia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 50: 607-617.
- Kehoe, E. G .; Toomey, J. M .; Balsters, J. H., & Bokde, A. L. (2012). Healthy aging is associated with increased neural processing of positive valence but attenuated processing of emotional arousal: an fMRI study. Neurobiol Aging.
- Zhang, L .; Qiao, L .; Chen, Q .; Yand, W .; Xu, M .; Yao, X .; Qiu, J. & Yang, D. (2016). Gray Matter Volume of the Lingual Gyrus Mediates the Relationship between Inhibition Function and Divergent Thinking. Front. Psychol, 7: 1532.
- Zilles, K. & Amunts, K. (2012). Architecture of the Cerebral Cortex. In: Mai, J. & Paxinos, G. (2012). The Human Nervous System. 3rd edition.