Potter syndrome or sequence: types, symptoms and causes
Different factors, including malformations in the kidneys, can interfere with intrauterine development and cause alterations in other body systems.
In this article we will talk about the causes, symptoms and types of Potter syndrome , name with which this phenomenon is known, often of genetic origin.
- Related article: "The differences between syndrome, disorder and disease"
What is the Potter sequence?
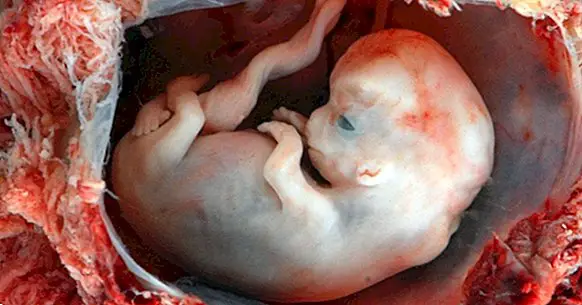
The terms "Potter sequence" and "Potter syndrome" they are used to refer to a set of physical malformations that occur in babies as a result of alterations in the kidneys, the absence of amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios) or compression during intrauterine development.
In 1946 the doctor Edith Potter described twenty cases of people without kidneys that also presented peculiar physical features in the head and lungs . Potter's contributions were key to raising awareness about this disease, more frequent than previously thought.
Potter believed that this type of physical malformation was always due to the absence of the kidneys, or renal agenesis; however, it was later found that there were other possible causes. The typological classification that we use today was developed around these and the associated alterations.
- Maybe you're interested: "How to take care during the first month of pregnancy: 9 tips"
Causes of this alteration
Frequently Potter syndrome It is associated with diseases and problems of the urinary system as the agenesis of the kidneys and the ureter, the polycystosis and the renal multicystosis or the obstruction of the urinary tract, which may be due to both genetic and environmental causes.
Many cases of Potter syndrome have a genetic origin (although not always hereditary); mutations have been identified in chromosomes 1, 2, 5 and 21 in the variants with bilateral renal agenesis, and similar causes have been identified in the other types.
The development of the classical variant consists of a series of interrelated events; this is why it is also called "Potter sequence". Incomplete formation of the kidneys and / or the ureter or rupture of the amniotic sac They make the fetus do not have enough amniotic fluid to form properly.
- You may be interested: "The 13 types of abortion and its psychological and physical effects"
Symptoms and main signs
Sometimes the signs that characterize Potter syndrome can be observed during intrauterine development. The most common is that medical tests reveal the presence of Kidney cysts or oligohydramnios or absence of amniotic fluid , which is usually due to the rupture of the sack that contains it.
After birth, the facial features described by Potter become evident: a flattened nose, epithelial folds in the eyes, a retracted chin, and abnormally low ears. In addition, alterations can occur in the lower and upper extremities. However, these characteristics are not always present in the same degree.
Potter syndrome is also associated with Malformations in the eyes, in the lungs, in the cardiovascular system , in the intestines and bones, especially in the vertebrae. The urogenital system is usually altered in a very significant way.
Types of Potter syndrome
At present, the different forms adopted by Potter syndrome are classified into five major categories or types. These differ both in the causes and in the nuclear clinical manifestations. On the other hand, it is important to mention also the classic form of this disease and that which is associated with multicystic renal dysplasia, discovered very recently.
1. Type I
This variant of Potter syndrome occurs as consequence of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease , a hereditary disease that affects the kidneys and is characterized by the appearance of numerous cysts of small size and full of fluid. This causes an increase in the size of the kidneys and interferes with the production of urine.
2. Type II
The main feature of type II is agenesis or renal aplasia, that is, the congenital absence of one or both kidneys ; in the second case, we speak of bilateral renal agenesis. Since other parts of the urinary system, such as the ureter, are also often affected, these signs are often referred to as "urogenital agenesis". The origin is usually hereditary.
3. Type III
In this case, malformations are due to autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (unlike type I, in which the disease is transmitted by recessive inheritance). Cysts are observed in the kidneys and an enlargement of their size, as well as an increase in the frequency of vascular diseases. Symptoms usually manifest in adult life .
4. Type IV
Potter type IV syndrome is diagnosed when cysts appear and / or water accumulates (hydronephrosis) in the kidneys due to a chronic obstruction of this organ or the ureter. It is a common variant during the fetal period that usually does not cause spontaneous abortion. The cause of these alterations can be both genetic and environmental .
5. Classic shape
When we talk about classical Potter syndrome, we are referring to cases in which the kidneys do not develop (bilateral renal agenesis), nor does the ureter. It has been proposed that the classic form described by Potter in 1946 can be considered an extreme version of type II, also characterized by renal agenesis.
6. Multicystic renal dysplasia
Multicystic renal dysplasia is an alteration characterized by the presence of numerous and irregular cysts in the kidneys ; in comparison with the term "polycystic", "multicystic" indicates a lower severity. In recent years cases of Potter syndrome due to this disorder have been identified that could indicate a possible new type.