Precentral rotation: characteristics and functions of this part of the brain
If we look at a photograph of a human brain, probably the first thing we see is the outermost layer, a wrinkled mass of grayish color. This outermost and superficial part is the cerebral cortex, and the aforementioned folds their convolutions or turns and their grooves.
These folds arise during the brain development of the fetus little by little, participating in the neuronal matter of which they are trained in different brain functions of great importance for our day to day. One of them easily identifiable is the precentral turn , which we are going to talk about throughout this article.
- Related article: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
The precentral turn: description and neuroanatomical localization
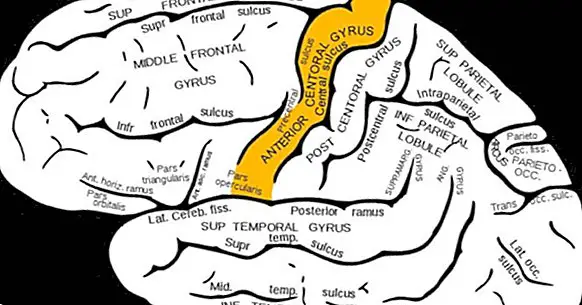
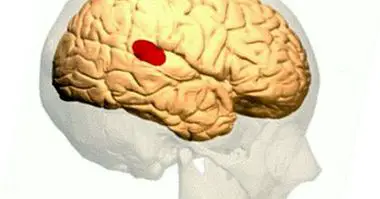
The precentral gyrus is one of the different cerebral twists or convolutions present in the cerebral cortex, being the part that at the observational level projects towards the outside of said folds. This turn is part of the primary motor area , so that its link with the ability to generate movement is relevant.
This brain region can be located in the frontal lobe , just ahead of the Rolando sulcus or central groove that separates frontal from parietal. For this reason another of the names of the precentral turn is that of prerrolándica rotation or convolution.
The precentral turn is present in both hemispheres , abutting with the Silvio fissure at the bottom. Right after the fissure we would find the postcentral turn, while more rostrally we would find the precentral sulcus or groove.
Functionally speaking, it would be deeply communicated with the secondary motor cortex and the supplementary motor cortex, which allow to plan and program the movement, and Broca's area, which allows to program movements linked to language. Also, also has connections to other brain areas such as the cingulate or hypothalamus .
In the precentral turn and part of the central groove or Rolando we can see represented the homunculus of Penfield, being both essential areas for the realization of the voluntary movement. Specifically, it is considered that the lower areas of the precentral turn control or innervate the head and face regions, while the upper parts are responsible for innervating the legs.
Another aspect to highlight of this turn is that in it we can find some of the largest pyramidal cells of the whole body, the Betz cells, reaching their axons to the spinal cord.
Associated functions
The precentral gyrus is a region of the brain that is very important when it comes to allow normative functionality and human behavior , being involved in various functions. Among them we highlight the following.
1. Voluntary movement
It is considered that in the precentral turn, identified with the primary motor cortex, there is motor representation and the first connections responsible for allowing the movement of different body regions. This brain region is due in large part to the impulse and the ability to move , both simple and complex.
2. Travel capacity
The ability to move or simply to interact with the environment physically is, due to the need for movement to perform, one of the different functions in which there is a participation of the precentral turn.
3. Language and communication
Our ability to communicate with others depends largely on the ability to move our muscles voluntarily, which depends largely on the action of the motor cortex which is part of the precentral rotation in order to talk (something which requires, among other things, the movement of lips and tongue) or communicate through gestures (musculature of the face and extremities).
4. Response to stimulation
Although the somatosensory system corresponds more to the postcentral gyre, the fact is that during experiments with monkeys it has been observed that in the precentral gyre we can also find regions responsible for giving a motor response to stimulation, specifically in order to seek protection or defense against possible threats . This effect has been observed with non-familiar stimuli, the cerebral response being less or non-existent before stimuli to which it is already accustomed.
Problems generated by your injury
The presence of lesions in the precentral turn can generate, as can be imagined, based on the importance of their functions, serious repercussions in the life of the sufferer. An example of this is the presence of paralysis in the form of monoplegia, hemiplegia, paraplegia or tetraplegia , being able to lose the ability to move different parts of the body.
It has also been observed that it has influence on the praxies or the performance of complex movements, causing the lesion of this rotation to cause apraxias. Likewise, the lesion of the precentral gyrus has also been associated with the presence of Broca's aphasia, making it impossible or complicated to produce the movements necessary to express oneself in a fluid way.
Bibliographic references:
- Graziano, M.S.A .; Alisharan, S.R .; Hu, X. & Gross, C.G. (2002). The clothing effect: Tactile neurons in the precentral gyrus do not respond to the touch of the familiar primate chair. PNAS, 99 (18): 11930-33.