Pyramidal neurons: functions and location in the brain
Neurons are the main type of cells that make up each of the elements of the nervous system. These structures are well known to most people today.
But although in the collective imagination we have a typical image or representation of what a neuron is, and many people imagine that all or almost all have the same structure and shape, the truth is that not all neurons are the same: there are very different types depending on their shape, where they send the information from, or even their relationship with other neurons. In this article we will focus on pyramidal neurons and in their functions .
- Related article: "Types of neurons: characteristics and functions
The pyramidal neurons
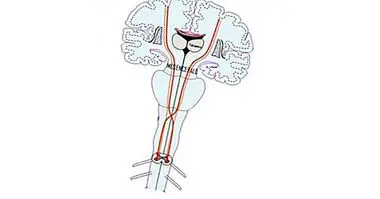
Pyramidal neurons are one of the different types of neurons present in our nervous system . It is one of the most common types of multipolar neurons, accounting for about 80% of the neurons in the cortex (not in vain, two of the layers of the cortex are called internal and external pyramids) and are found between some of the most relevant of the organism. They are usually considered projection neurons. That is, they act by sending the message to cells that are far away and separated from the area where they are born.
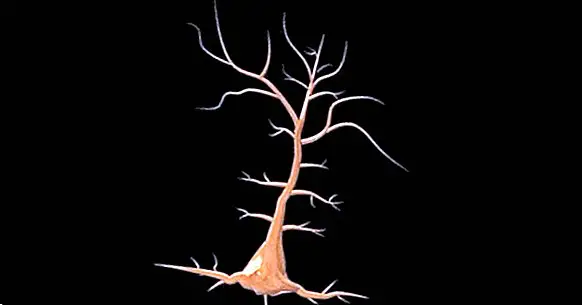
Discovered by Santiago Ramón y Cajal , the name of this type of neuron refers to the shape of its soma, with a triangular or pyramidal appearance. They are mostly glutamatergic neurons, with glutamate being the neurotransmitter that activates them, and they usually act as excitatory type neurons. They can have different sizes, the largest being the giant pyramidal or Betz cells.
Like other neurons, the structure of this type of neurons consists of soma, which, as we have said, has a pyramidal shape, an axon and dendrites. However, they have a particularity: in regard to the dendrites, they have a fairly long compared to the rest, called apical dendrite , and numerous basal and shorter dendrites that are going to branch off.
- You may be interested: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
Location of these nerve cells
Pyramidal neurons can be found at different points in the nervous system, but they are much more prevalent in some specific areas. Among them, the following stand out.
1. Brain cortex
The pyramidal neurons are found largely in the cerebral cortex, forming part of most of this and found in five of the six layers that make up this brain region. Specifically, they can be observed in the granular and pyramidal layers, both external and internal.
They stand out especially in the third and fifth layers (which are what are in fact called external pyramidal and internal pyramidal), being larger as the deeper in the crust are. Within the crust, likewise, there are areas where its existence has been detected more often.
2. Motor cortex
In the motor cortex we can find a large number of pyramidal neurons, being especially linked to motor control. In this area of the cortex there are many known as Betz cells , giant pyramidal neurons that carry the motor information from the brain to the areas of the spinal cord where they synaptan with the motor neurons that activate the movement.
3. Prefrontal cortex
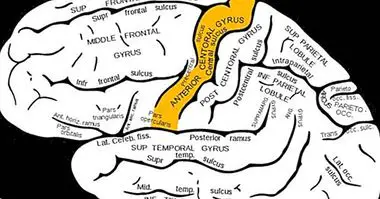
Pyramidal neurons can also be found in the prefrontal cortex, influencing higher mental processes. It is considered that these cells they are the main primary excitation neurons of the prefrontal , participating in numerous functions and considering themselves primordial for the existence of behavior control.
4. Corticospinal tract
The pyramidal neurons are especially visible along the corticospinal tract, which sends the motor information from the different brain nuclei in charge of motility to motoneurons that will generate muscle contraction, passing through the spinal cord.
4. Hippocampus
Not only in the cortex can we find pyramidal neurons, but also the we can find in subcortical structures . One of them is the hippocampus, linked to aspects such as memory and orientation.
- Related article: "Hippocampus: functions and structure of the organ of memory"
5. Amygdala
Another of the structures in which these neurons are found is in the cerebral amygdala, an area of the limbic system linked to emotional memory.
Functions of pyramidal neurons
Like the rest of the neurons, the pyramidal ones are structures that transmit information in the form of electrochemical pulses that will be captured by other neurons until they reach their final destination.Being a type of neuron so prevalent in the cortex, pyramidal neurons are activated and are linked to a large part of the functions and processes carried out by the human being. Examples of such functions are the following.
1. Movement
Motor control is one of the functions that has traditionally been associated with pyramidal neurons. Specifically, these neurons are deeply associated with the voluntary motor control of the muscles.
2. Cognition and executive functions
The excitatory role of pyramidal neurons in the prefrontal cortex means that their activation can be linked to cognitive processes of great relevance, like executive functions or cognition .
3. Emotion
The activity of pyramidal neurons in the prefrontal cortex is linked to the connection of these areas with different subcortical regions, among them the limbic . In this sense, the amygdala and the hippocampus have a fundamental role.
4. Memory and orientation
Memory and special orientation are other functions in which a great activation occurs in pyramidal neurons, in this case those of the hippocampus.
Bibliographic references
- Kandel, E.R .; Schwartz, J.H. & Jessell, T.M. (2001). Principles of neuroscience. Fourth edition. McGraw-Hill Interamericana. Madrid.
- McDonald, A.J. (1992). Cell types and intrinsic connections of amygdala. Prog. Neurobiol. 55: 257-332.