Reticular formation: characteristics, functions and associated diseases
Many of the structures of the brain can be easily located and separated from the rest. However, there are others that, being more distributed by several parts of the brain, cost more to detect.
The reticular formation is one of these although the fact that it is more discreet does not mean that it is less important. In fact, we need it to live and be aware of what happens to us.
Next we will see the characteristics of the reticular formation, its functions and the problems that can appear if something interferes in its state due to illness or injury.
What is reticular formation?
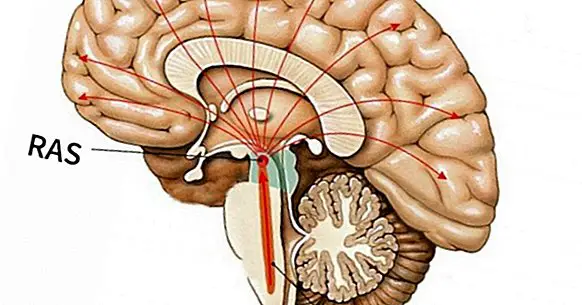
The reticular formation is a network of neurons that lies between the trunk of the brain and the diencephalon specifically the thalamus. That is, it is located in one of the lower parts of the brain, and therefore has a fundamental role in everything that happens in the higher areas.
Since the reticular formation is a network of neurons, its boundaries and borders are diffuse, and it is not easy to know where it begins and where it ends. For example, the naked eye is practically impossible to locate, and in any case it is possible to see in an approximate way the structures by which it is distributed.
It is considered that the "starting point" of the reticular formation is a part of the brainstem called an annular protuberance, between the medulla oblongata and the mesencephalon, and from there it rises until it reaches the thalamus, opening more and more like a fan. This formation is constituted by a hundred of groups of neurons scattered in an irregular way by the nervous tissue of these zones.
Functions
The reticular formation has a fundamental role when it comes to regulating the level of consciousness that we have , a process in which also intervenes especially the thalamus. This means that his work has to do with the circadian rhythm and the appearance and disappearance of sleep, among other things.
On the other hand, another of the functions of this network of neurons is the regulation of the state of excitation, or state of alertness, a process parallel to that of the regulation of the conscious state.
As the reticular formation is at the entrance to the brain through its areas closest to the spinal cord, it also acts by filtering the information that is arriving from the senses, selecting pieces of data and discarding irrelevant parts, which do not reach the conscience In the same way, its relation with attentional and consciousness processes causes it to intervene in the perception of physical pain and in the processes of habituation to repetitive stimuli.
Further, reticular formation influences involuntary and automatic movements , as those that serve to maintain vital signs (heartbeats, for example). In that sense, it is one of the components of the nervous system without which we could not live.
His parts
The reticular formation can be divided into the following parts.
1. Core group of cores
A region of the reticular formation that in turn divides into posterolateral nuclei and medial nuclei.
2. Side group of cores
Divided into the reticular nucleus of the pontic tegmentum, lateral nucleus and paramedian.
3. Medium group of cores
Also known as raphe nuclei, located in the medial area of the brainstem. It is divided into the dark nucleus of the raphe and the great nucleus of the raphe.
Diseases associated with reticular formation
The diseases that affect the reticular formation are usually very serious, since the interference with this brain region produces coma or death.
For example, advanced Parkinson's disease can damage this network of neurons, since it expands throughout the nervous system. In the same way, narcolepsy, directly involved in the altered states of consciousness, produces harmful effects in the reticular formation.
Another disease related to this neural network is cataplexy , whose main symptom is the loss of muscle tone; In some way, in the waking state, the body begins to behave as if it were in a REM sleep phase, which means that the brain is disconnected from the muscles.
Beyond the diseases linked to processes of deterioration of unknown causes or the action of viruses, the lesions can also seriously alter the functioning of the reticular formation, leading to coma or brain death in a large number of cases.
This is one of the most vulnerable areas of the nervous system , not only because it intervenes directly in the state of consciousness, but because it participates in the maintenance of basic vital functions without which there is a sudden death due to hypoxia in the brain. That is why the functioning of this region is considered an indicator of the presence of life more reliable even than the recording of electrical activity by means of techniques such as the EEG in more superficial areas of the cerebral cortex.