Subtlalamus: parts, functions and associated disorders
The human brain is configured by a large number of structures and substructures that account for different body systems and different cognitive and emotional abilities and abilities. All the information we collect For example, it must be integrated in order to form a concrete representation of reality. Of the same that also must integrate different processes at the time of giving answer to the environmental stimulation.
There are different relay centers where such associations are made, such as the thalamus. But in addition to this there are different brain structures with similar functions, such as the subthalamus .
- Related article: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
What is the subthalamus?
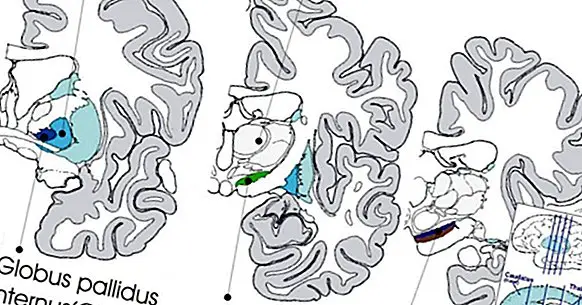
The subthalamus is a complex structure linked to the management of body movement and that it has a great multitude of connections with different brain regions, such as the substantia nigra and the red nuclei, although some of its most important connections are with the pale globe.
This structure is part of the diencephalon and it is located between the brainstem and the cerebral hemispheres. Specifically, it can be found below the thalamus, from which it is separated by the limiting interthalamic zone, and above the mesencephalon (specifically the tegmentum). It also connects with the hypothalamus.
In addition to those already mentioned, other structures with which the subthalamus is connected include the motor and prefrontal cortex or the basal ganglia.
- Related article: "Diencephalon: structure and functions of this brain region"
Main divisions of the subthalamus
The subthalamus can be divided into the different structures that make it up . The main sections that can be considered within this brain region are the following.
1. subthalamic nucleus
One of the main structures of the subthalamus, the subthalamic nucleus, is a nucleus of oval shape that can be localized in the central part of the uncertain zone (which we will discuss later). This brain region has great importance due to the large number of afferences it receives. The most relevant due to its link with the management of the movement is the relationship he has with the basal ganglia , with which it interacts through the use of glutamate.
It also has glutamatergic connections to the primary, prefrontal and premotor motor cortex, as well as to the thalamus and reticular formation.
2. Uncertain area
Located between the lenticular and the thalamic fasciculus, the uncertain zone is one of the substructures of the subthalamus. This sheet-shaped core is involved in the control of movement, forming part of the extrapyramidal pathway and in connection with the motor cortex . At its center is the subthalamic nucleus
3. Forel cores
Nuclei of the Forel areas are three small areas of white matter of the subthalamus, also called Forel fields , which act as nerve projections to different regions brain regions.
Principal functions
The subthalamus is a structure of great importance for the correct functioning of the human being, having a great role in the integration of the motor information that allows the management of the movement. Especially it is linked to Involuntary aspects of movement and precise control of it , greatly affecting its connection and influence with the basal ganglia.
In addition to motor control, it has also been observed that the subthalamus influences orientation and balance , being observed before his injury a greater risk of falls before the injury of the uncertain zone.
Lesions in the subthalamus
The presence of subthalamic lesions usually cause Symptomatology linked to movement control . In general, an injury in this area tends to produce sudden and involuntary movements, such as spasms and choreic movements of the extremities.
Regarding the latter, the subthalamus injury is especially linked to Huntington's chorea, in which the subthalamic nucleus is especially affected. The same happens in the Sydenham chorea , of infectious origin. The degeneration of this structure causes the choreic movements typical of these diseases.
It is also observed that the injury of the subthalamus in its connection with the pale globe can generate hyperkinesia or excessive uncontrolled movements. On the other hand, it has been proposed that the stimulation of this region could be useful when it comes to alleviating Parkinson's symptoms or other movement disorders, due to its effect on aspects such as locomotion and posture, through transcranial magnetic stimulation.
- Related article: "Parkinson: causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention"
Bibliographic references:
- Snell, R.S. (2006). Clinical Neuroanatomy. 6th edition. Editorial Panamericana Medical. Madrid.
- López, L. (2003). Functional anatomy of the nervous system. Noriega Editors. Mexico.
- Afifi, A.K. & Bergman, R.A. (2007). Functional neuroanatomy. 2nd edition. Mc Graw-Hill Interamericana.