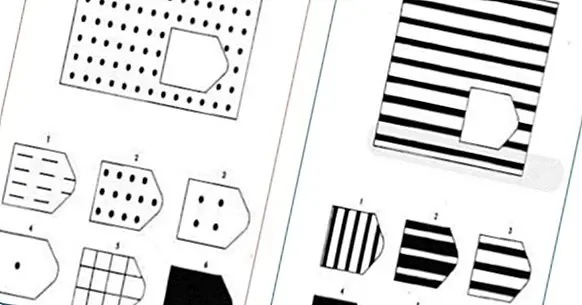
Test of progressive matrices of Raven
There are few issues within the world of psychology that raise as much controversy as the study and evaluation of human intelligence . The dispute about whether it is possible to measure the intelligence of a person based on a single construct or if there really is a general intelligence persists to this day.
However, the tests that try to measure human intelligence are the most used in any area of evaluation. Being the test of matrices of Raven is one of the acclaimed and appealed for its ease of application and its versatility.
What is the Raven progressive matrix test?
The Raven progressive matrices test is a test more than known and used in the psychological and psychopedagogical field. This test, designed in 1938 by the English psychologist John C. Raven, had the objective of calculating the "G" factor of intelligence and its administration was restricted to the officers of the United States Navy.
The "G" factor of intelligence refers to the general intelligence that conditions any execution or resolution of problems , and is common to all the skills that require an intellectual component. This factor demonstrates the ability of a person when doing an intellectual job.
The main characteristic of this test is to encourage the analytical reasoning, the perception and the capacity for abstraction. In addition, being a non-verbal test uses the comparison between forms and reasoning by analogies, without the need for the person to need a culture or prior knowledge.
At present, there are different versions of this test, which are administered depending on the age and skills of the person to be evaluated. These three versions are: The general scale for people between 12 and 65 years old
- Progressive color matrices for children between 3 and 8 years old with some kind of intellectual functional diversity
- Advanced matrices for the evaluation of people with above average capabilities
Test characteristics
There are a number of distinctive features that have made this test one of the most used. These characteristics are given at the level of administration, objectives and reliability
1. Objective
Another objective of the Test of progressive matrices of Raven is to measure the eductive capacity of the person , which we will explain later, by comparing forms and using reasoning by analogy; all this independently of the knowledge previously acquired by the subject.
2. Material
It is a test that uses series of abstract and incomplete geometric figures that are presented to the person gradually and with ascending difficulty. The test can be administered through printed cards or also virtually.
3. Administration
Another advantage of this test is that it is capable of being self-administered, as well as being administered both individually and collectively.
The time of application of this test is between 30 and 60 minutes, however this is usually completed 45 minutes after its start.
4. Reliability and validity
Finally, regarding the reliability and validity of this test, it presents a 0.87-0.81 reliability, while in validity an index of 0.86 was obtained. These data were obtained with the Kuder-Richardson formulas and with the Terman Merrill criteria.
In what contexts is this test administered?
The Raven progressive matrix test is used as a basic and applied evaluation tool, and its administration can be extended to many and diverse fields. However, the contexts in which this test is most used are:
- Teaching centers
- Work orientation and personnel selection centers
- Psychological clinics
- Psychological, sociological and anthropological research centers
- Military and defense contexts
Purpose of the test: the ability to eduction
As discussed at the beginning of the article, one of the main objectives of the test is to test and measure the person's educational capacity.
This eductive capacity refers to the ability of people to find relationships and correlates within information that is presented in a disorganized and poorly systematized manner in which these relationships are not immediately evident.
The capacity of eduction is associated with the intellectual capacity for the comparison of images and representations, as well as with the analogical reasoning , without taking into account the cultural level or knowledge that the person possesses.
This ability constitutes the most important spring in the high level cognitive functioning, which is involved in the different processes of abstraction.Likewise, if we compare it with other related concepts, the ability to eduction is the one that most resembles fluid intelligence.
What is this test based on? The two-factor theory of Spearman
The English psychologist Charles Spearman established the existence of a general intelligence in the year 10904. Based on his research, Spearman indicated that the "G" factor of intelligence was the main person in charge of the general intellectual performance of the person.
Spearman believed that if a person is able to excel in certain areas or cognitive activities, it is likely that they will also do so in almost all areas. For example, a person with good scores in numerical tests, is very likely to also get high scores in logic tests or verbal tests.
Following here developed a theory known as Bifactorial Theory, according to which within human intelligence can be distinguished two fundamental parameters: the general factor or factor "G" and the special factor or factor "S".
Factor "G"
The general factor refers to a personal and possibly hereditary quality . It consists of a special attribute of the brain that differs from one person to another but that remains stable throughout the life of the person.
"S" factor
This factor covers the specific skills or abilities that a person has to face any type of task . Unlike the "G" factor, it differs according to the person's previous education and can not be extrapolated to other areas.
However, the controversy surrounding these constructs is not small, since some sectors maintain the idea that there can not be an idea of general intelligence and that this is only a sample of the opportunities that a person has had to learn certain skills or acquire certain knowledge.