The 4 phases of mitosis: this is how the cell doubles
The cell is the unit of life. Probably, one of the fundamental characteristics of these is the ability of these living beings when it comes to self-reproduction.
All cells reproduce by dividing into several daughter cells, which in turn can continue to proliferate. In the case that pertoca us for being human, that is, in eukaryotic cells, there are two types of division: mitosis and meiosis. For this occasion, I will focus on the first one and I will explikcaré the phases of mitosis that he performs to carry out the formation of two daughter cells.
- Related article: "Differences between mitosis and meiosis"
The common phase
The cells follow the pattern of a sequential process that concludes in cell division . This process is known as the cell cycle. In a summarized way, the cycle consists in preparing the cell for its imminent partition of two. This process has traditionally been divided into two major phases: the interface and the M phase. The latter would properly be the phase of mitosis. The interface is shared both in mitosis and in meiosis.
If the eukaryotic cell cycle takes 24 hours, the interface would occupy 23 of these, leaving only one hour for its division. It is normal that it takes so long, since during this stage the cell doubles its size, doubles its genetic content and prepares the necessary tools so that everything goes well in the formation of new cells.
The interface, in general, is divided into three stages:
- Phase G1 (Gap1): the cell grows in size and is metabolically active .
- Phase S (Synthesis): the cell replicates its DNA.
- Phase G2: the cell continues to grow and synthesizes proteins that will be used for mitosis .
Once the cell enters the S phase, there is no turning back in the process of division, unless it is detected that its DNA is damaged. Cells have signaling systems that allow the recognition of their DNA and if something goes wrong, stop the process to avoid causing major problems. If all is well, the cell is already prepared for its imminent proliferation.
Phases of mitosis
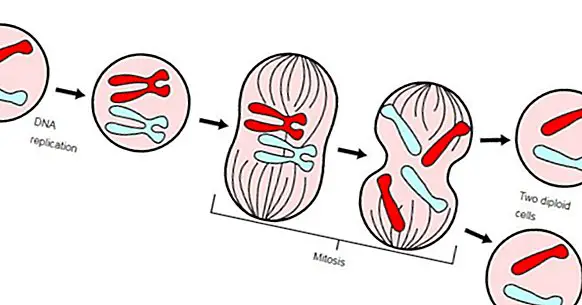
After finishing the interface, the cell enters the M phase with the aim of forming new cells . Mitosis results in two sister cells of equal genetic content. Mitosis has differences according to the eukaryotic cell that makes it, but all have in common the condensation of chromosomes, the formation of the mitotic spindle and the union of chromosomes to the latter ... many new concepts that I will clarify.
Traditionally, mitosis has been divided into four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. To explain this process I will focus on the case of human cells.
1. Profase
At the start of Phase M, the replicated DNA that it is entangled it condenses into a more compact form known as a chromosome . In the case of humans we have 23 chromosomes. As it is still preparing to split, the chromosomes are still formed by the two chromatids (the original and the copy), joined by a midpoint known as centromere, giving the typical image of an X.
Not only this happens; It should be remembered that the genetic material is found inside a nucleus , and to be able to access it, it is necessary to degrade the membrane that surrounds them. In addition, the mitotic spindle is generated, a set of filamentous protein structures (microtubules), which will subsequently act as transport pathways for the chromosomes.
- Maybe you're interested: "Differences between DNA and RNA"
2. Metaphase
When these mentioned microtubules bind to the centromere of the chromosomes and they are aligned right in the center of the cell when the metaphase occurs. It is already at the point where the genetic content is separated. It is a phase of mitosis that is rapid.
3. Anaphase
In this phase of mitosis you will understand how the mitotic spindle acts. What it does is separate the sister chromatids and drag them to opposite poles, as if they were a fishing rod that is picking up the line. In this way, it is possible to have the same genetic content in the two new cells.
4. Telophase
Once on opposite sides, the chromosomes are decondensed in their usual way and the nucleus that contains them is regenerated. Along with this cytokinesis occurs, that is, the division into two cells . This process begins at the end of anaphase, and consists of the case of animal cells in a contractile ring that strangles the cell membrane more or less in the center, like a balloon, until two independent cells are generated.
The final result of mitosis is the formation of two interphase sister cells, since they contain the same genetic content and there has been no modification of this, it has simply been replicated . It should be noted that any anomaly in this process stops him immediately.