Trichomoniasis: symptoms, causes and treatment of this STD
Although there is a large amount of information today regarding sexually transmitted diseases and infections, these types of alterations continue to be spectacularly frequent in the population around the world.
Some, such as HIV / AIDS, continue to be an epidemic that ends or greatly alters the lives of millions of people and that do not have a curative treatment. Others fortunately can be cured, although they are often socially undervalued. One of the latter is trichomoniasis , of which we will mention throughout this article.
- Related article: "HIV and AIDS: psychological effects of this disease"
One of the most common STDs: trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) , despite not being the best known at the social level.
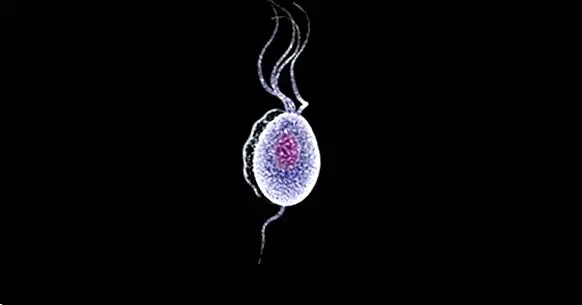
This disease is caused by a protozoan parasite that is transmitted through vaginal sex and that infects the genitourinary tract. Trichomoniasis may or may not have obvious symptoms, often being unnoticed by the person in question. In fact, this is what happens in about seven out of ten cases.
Between the infection or contagion and the beginning of the possible symptoms there is an incubation period of between five and twenty-eight days. It can appear in both men and women, although in the former it is usually asymptomatic. Often the symptoms are so mild that they confuse them with other problems, and they may appear and disappear intermittently.
When symptoms do occur, it should be borne in mind that in the first place one of the possible alterations generated by this disease is the appearance of inflammations such as vulvitis, vaginitis or urethritis , it is also usual that anomalous secretions appear.
In women it is common for trichomoniasis to generate discomfort, burning and pain in the genitals when urinating or having sex, along with possible secretions usually greenish or yellowish and smelling foul. There is also dysuria or difficulty urinating, bleeding and macules on the surface of the vagina.
In the case of men, in the few cases where there are symptoms, pain and burning appear when urinating or ejaculating, difficulties to urinate or dysuria and the need to urinate many times during the morning. Purulent secretions may also appear on the penis. Occasionally it can generate inflammation of the prostate .
- Maybe you're interested: "Sex phobia (erotophobia): causes, symptoms and treatment"
Possible complications
In any of the cases and especially in the case of women, trichomoniasis can have relevant repercussions for health.
In pregnant women it has been seen that it can cause prematurity and low weight in the newborn, and the disease can even be transmitted to the fetus.
Likewise, in both sexes it facilitates the appearance of wounds and the transmission or transmission of other venereal diseases, including HIV. In fact, it is not uncommon for this infection to appear together with others like gonorrhea.
Causes and transmission of this disease
Trichomoniasis is a disease caused by the infestation of a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis , and is contracted through the maintenance of unprotected sex.
Generally the parasite is transmitted through vaginal penetration. It is not limited only to sex between heterosexual people, being able to transmit also during relations between people of the same sex (being able to also pass from vulva to vulva without there being penetration). It can also be transmitted by sharing sex toys or by manipulating one's own or someone else's genitals after touching infected fluids.
However, it is at least uncommon for the infection to be transmitted through anal or oral sex, usually not affecting the mouth or anus. Casual contact, sitting in the same sink, eating or drinking from the glass world or contact with saliva through kissing or sneezing are also not routes of transmission of this disease.
In addition to all the above, we must bear in mind that It is very simple and usual for a person with this disease to infect his partner , and that even if it is treated it can be reinfected by it again. In this sense, it is essential that when trichomoniasis is detected, both the person and his or her sexual partners are treated.
Treatment
Trichomoniasis is fortunately a disease that has effective treatment, being easily curable. Specifically, said treatment is based on the prescription and taking of antibiotics .
One of the most common is in tinidazole, which eliminates and prevents the multiplication of the protozoa that causes the disease (it is also used in other venereal diseases). The other is metronidazole, which can be prescribed in cream or tablets.There are versions in which one dose of the drug is sufficient, although daily doses may be required. The disease usually subsides about a week after starting to apply the treatment, although symptoms can be seen as early as the second day.
As we have indicated previously, it is fundamental that the treatment is carried out by both members of the couple at the same time. Sexual contact should be avoided until the disappearance of the causative organism is observed . Also the consumption of alcohol and other substances, since they interfere in the operation of the drug.
In any case, the easiest way to avoid possible diseases like this is in prevention, using prophylaxis such as condoms or other barrier methods.
Bibliographic references
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (s.f.). Trichomoniasis: CDC fact sheet. [On-line]. Available at: //www.cdc.gov/std/spanish/tricomoniasis/stdfact-trichomoniasis-s.ht.
- Hobbs, M., Seña, E.C., Swygard H. & Schwebke, J. (2008) Trichomonas vaginalis and Trichomoniasis. In: KK Holmes, PF Sparling, WE Stamm, P Piot, JN Wasserheit, L Corey, MS Cohen, DH Watts (editors). Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 4th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 771-793.