Trifluoperazine: uses and side effects of this antipsychotic drug
Trifluoperazine is a drug that is prescribed to treat some manifestations of schizophrenia. This is because it has important effects in the mesolimbic pathways that regulate the release of dopamine. It is likewise a drug that is not marketed anywhere and that is subject to medical prescription.
In this article we will see what is trifluoperazine , how it acts in the limbic system, what its indications and side effects are.
- Related article: "Types of psychotropic drugs: uses and side effects"
What is Trifluoperazine?
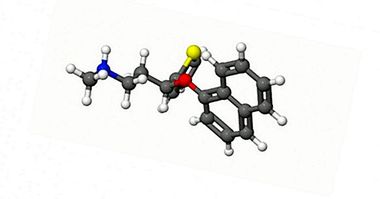
Trifluoperazine is a chemical compound of antidopaminergic reaction. That is, it acts as an antagonist of dopamine receptors, which has tranquilizing, anxiolytic and potent antipsychotic effects.
For these effects, trifluoperazine is within the group of typical antipsychotics , which are also called conventional antipsychotics with neuroleptic effects (depressants of the central nervous system).
Very roughly it is a drug that decreases the excitation of electrical activity in the brain.
- You may be interested: "Types of antipsychotics (or neuroleptics)"
What is it for and in what disorders is it used?
Trifluoperazine is prescribed to treat some manifestations of the diagnosis of schizophrenia and its main objective is to reduce psychotic experiences. Because of its important sedative action, it is commonly recommended in acute schizophrenia crisis with intense anxiety and mania. Its non-prolonged use is also recommended to treat anxiety symptoms that have not responded to other medications.
This medicine is acquired with medical prescription and is marketed under different names, depending on the country. Some of the most common are Cuait Trifluoperazine, Eskazine, Stelazine, Tristazine and Stelazine and its presentation of tablets for oral administration. In the case of Spain, it has stopped being commercialized since the beginning of 2018. However, there are some generic presentations and it is also distributed by import.
- You may be interested: "What is schizophrenia? Symptoms and treatments"
Mechanism of action
Although this mechanism is not precisely defined, different investigations have linked the anti-dopaminergic actions with the decrease of psychotic experiences. The "antidopaminergic actions" are those that produce a blockade of the postsynaptic receptors in the mesolimbic cortical pathways.
The latter is one of the dopaminergic pathways of the brain that begins in the mesencephalon and ends in the limbic system (passing through the amygdala, the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex, among other areas). The mesolimbic pathway is one that has been significantly related to situations such as emotional regulation, motivation, emotional gratification and reward mechanisms . The main neurotransmitter that acts within this pathway is dopamine.
For its effects in terms of emotional and behavioral regulation, the activity of the mesolimbic pathway is associated with the behavioral and psychic manifestations of schizophrenia . More specifically with the manifestations of what has been called "positive symptoms" or "psychosis", where the experiences of hearing voices or depersonalization, among others, are very present.
There is a dopaminergic hypothesis that says that these last experiences are related to an overactivity of the mesolimbic pathways in the brain, with which drugs such as trifluoperazine, which act as blockers of dopamine receptors, have been developed. It is expected that long-term trifluoperazine can prevent new psychotic outbreaks.
Side effects and contraindications
The dopaminergic action not only has neuroleptic effects in the decrease of psychotic manifestations, but also has effects in other neuronal receptors and in other systems beyond the central nervous system, for example in the endocrinological system or the metabolic system.
Within the central nervous system, and while trifluoperazine also impacts other pathways (not only mesolimbic), it can produce some reactions such as drowsiness, dizziness, decreased alertness and reaction capacity, photosensitivity and some visual disturbances.
In addition, the use of trifluoperazine can generate more serious adverse reactions such as constant and involuntary motor agitation , combined with periods of extremely slow movements.In relation to other systems, such as the metabolic or endocrine can cause constipation, reduced sexual activity, hyperglycemia, among other reactions.
In the case of prescription or taking excessive doses, as well as in the case of abrupt withdrawal of the drug, there have been seizures, loss of consciousness, fever, tachycardia and liver failure in high doses, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, among other reactions adverse that can be deadly.
Its use is not recommended during pregnancy and lactation and should avoid mixing with other narcotics, anesthetics, sedatives and alcoholic beverages (otherwise it increases the likelihood of adverse reactions).
Older adults are especially sensitive to the effects of this medication so it is recommended to take special precautions in this case. It is especially contraindicated in the case of people with dementia (because it increases the risk of cardiovascular accident and mortality), it is used only in case other pharmacological options have not worked and it is recommended not to prolong the treatment for more than 3 months. The same in the case of people who have glaucoma, angina pectoris and other associated medical conditions.
Bibliographic references:
- Marques, LO., Lima, MS. & Soares, BGO. (2004). Trifluoperazine for schizophrenia. Cochrane Retrieved June 15, 2018. Disponiboe at //www.cochrane.org/en/CD003545/trifluoperacina-para-la-esquizofrenia.
- Psicofarmacos.info (2018). Classification of antipsychotics. Retrieved June 15, 2018. Available at //www.psicofarmacos.info/?contenido=antipsicoticos&farma=eskazine-stelazine-estelazina-triftazina.
- Vademecum (2015). Trifluoperazine Retrieved June 15, 2018. Available at //www.vademecum.es/principios-activos-trifluoperazina-n05ab06.