Trigeminal neuralgia: symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment
There are few pains that cause as much disability and discomfort as pain related to the ear or toothaches. Luckily for the person who suffers, these are temporary and can be easily remedied.
Now, imagine that these pains appear in a fortuitous and chronic way and that, in addition, the treatments could not get the pain to permanently subside. This is what happens in trigeminal neuralgia, a very painful disorder which we will talk about next.
- Related article: "Cranial pairs: the 12 nerves that leave the brain"
What is trigeminal neuralgia?
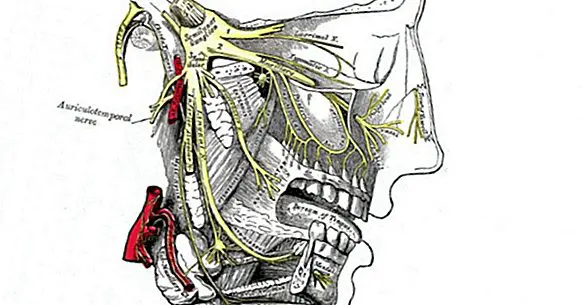
The condition known as trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic and lacerating condition that is caused by an alteration in the trigeminal nerve or fifth cranial nerve . This trigeminal nerve is one of the longest nerves in the skull.
Among the effects that trigeminal neuralgia causes in the person is a sensation similar to the one that causes the burning, which appears suddenly and fortuitously (Type I); In addition, these patients may also experience a sensation of intense, throbbing pain that can last up to two minutes (Type II). Hence, this disease is also known as Tic dolorosa.
The pain caused by this condition can reach such intensity that the person is practically incapacitated both physically and mentally.
To understand this condition well, it is necessary to know that this trigeminal nerve forms part of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves that start from the base of the skull. Its function is to transport sensations between the brain and the upper, middle and lower parts of the face and the oral cavity. This nerve is formed by three ramifications:
- The ophthalmic branch or higher transports the sensations to almost the entire scalp, to the forehead and to the front area of the head.
- The maxilla or media branch it crosses the cheek, the upper jaw, the upper lip, the teeth, the gums and the sides of the nose.
- The mandibular branch or lower It runs through the jaw, teeth, gums and lower lip.
In trigeminal neuralgia, more than one nerve branch may be affected causing intense pain in any of the areas mentioned above.
- Related article: "The 13 types of pain: classification and characteristics"
What symptoms does it present?
As previously mentioned, the symptomatology associated with trigeminal neuralgia is distinguished by causing a patient suffering or lacerating and acute pain, similar to an electrical shock that It is usually felt on one side of the jaw or on the cheek .
These episodes of pain can occur on either side of the face. However, they never manifest on both sides at once. The complete symptomatology that can occur in trigeminal nerve neuralgia includes:
- Contractions that cause very intense pain , like an electric shock, of a duration of up to two minutes and that can appear constantly.
- Usually pain only appears on one side of the face . Specifically in the eye, the cheekbone and the lower area of the face.
- When the pain appears there is no type of subsequent numbness and the ability to move the affected face area is also not lost .
In most cases, patients can predict the appearance of the episode since it tends to be preceded by sensations of tingling, stiffness or a slight but continuous pain sensation.
One of the main characteristics of this symptomatology is that it appears suddenly and randomly. However, these incidents can be triggered by a vibration or contact with the cheek caused by any daily action such as washing the face or teeth, eating or even talking.
Although the trigeminal neuralgia does not per se pose a risk to the health of the person, the pain it causes can become highly disabling, causing that the person rejects by all the means to perform those daily tasks that may cause a new crisis .
What causes this type of neuralgia?
Although in many cases the cause of trigeminal neuralgia remains undetermined, There are a series of situations and diseases that lead to the appearance of these episodes of pain so characteristic.
The contexts in which it can appear are:
- Trigeminal nerve compression by a blood vessel: this compression can occur either by the normal aging process itself or by the presence of a tumor.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) or other diseases that cause the deterioration of myelin.
- Trigeminal nerve injury due to trauma or surgery of the mouth or sinuses.
How is it diagnosed?
At the moment, no specific type of test has been developed for the diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia.
The steps to follow to make an accurate diagnosis of trigeminal neuralgia are:
- Exploration of medical history of the person.
- Description of symptoms.
- Physical exam.
- Comprehensive neurological examination .
- Performing neuroimaging studies to rule out the action of a brain tumor or multiple sclerosis.
What is treatment and what is the prognosis?
As with the diagnosis, a treatment that has the ability to permanently eliminate pain caused by trigeminal neuralgia has not yet been discovered.
However, there are several treatments or interventions that can significantly improve the patient's situation . These treatments are pharmacological therapy, surgery and other treatments or remedies.
1. Pharmacological therapy
There are certain medications that tend to reduce pain and the number of attacks. Among these medications are:
- Anticonvulsant medication It is the most effective and may include carbamazepine, topiramate or gabapentin.
- Administration of opioids such as methadone when neither anticonvulsants nor surgery works.
- Treatment through the use of low doses of antidepressants like nortriptyline.
- Derivatives of morphine such as dolantine.
- Botox injections in the nerve.
2. Surgery
A second option is the solution through certain types of surgeries. However, the effectiveness of its results is widely discussed by the medical community.
The main practice carried out in trigeminal neuralgia is microvascular decompression (VDM), by which the surgeon places an element between the nerve and the blood vessel that makes pressure.
Other strategies consist of undoing or sectioning some areas of the nerve root using the following techniques:
- Glycerol injection .
- Radiosurgery
- Radiofrequency ablation.
- Microcompression with percutaneous balloon.
3. Other remedies
The person affected by trigeminal neuralgia can also benefit from the effects of alternative treatments such as acupuncture or chiropractic combined with medication, because of the suggestion . Likewise, the use of capsaicin creams, the modification of eating habits or cyanocobalamin supplements may also be useful to reduce the intensity of symptoms.