Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone): these are its functions
Hormones are chemical compounds that, when released by the endocrine glands in the blood or nervous system of living beings, exert modulating effects on the functions of other cells and body structures.
One of the most relevant and known human hormones is vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone, which is essential for fluid retention or stress response, among other phenomena. In this article We will analyze the properties and functions of vasopressin .
- Related article: "Types of hormones and their functions in the human body"
What is vasopressin?
Vasopressin is also known as "Argipressin", "arginine vasopressin" and "antidiuretic hormone" . As this last name suggests, this hormone fulfills functions related to the reabsorption of water molecules through the kidneys and with the decrease in the amount of urine accumulated in the organism.
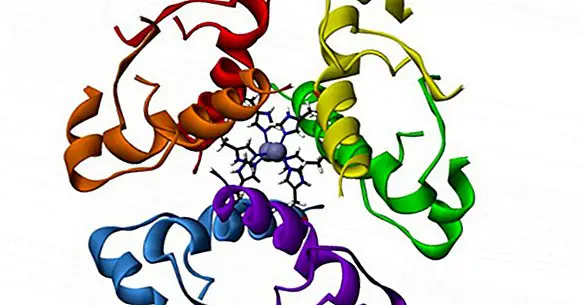
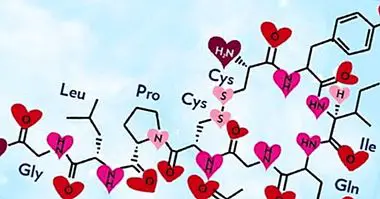
It is an oligopeptide, that is, a molecule composed by the union of a small number of amino acids, specifically 9. In contrast, the polypeptides are sets of between 10 and 100 amino acids, while "proteins" are used to refer to to groupings of more than 100 molecules of this type.
Specifically, vasopressin contains an amino group (-NH2), cysteine (Cys), tyrosine (Tyr), phenylalanine (Phe), glutamine (Gln), asparagine (Asn), proline (Pro), arginine (Arg) and a carboxyl group (-COOH).
Vasopressin is secreted by the neurohypophysis , the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland, in response to changes in the osmotic concentration and in the volume of the blood. Although most of the vasopressin we produce is released into the bloodstream, its effects on the brain also explain some of its functions.
Other pituitary hormones
The pituitary or pituitary gland is one of the main endocrine glands . It fulfills an intermediary function between the hypothalamus, which initiates the secretion of hormones, and the rest of the endocrine system by sending biochemical signals.
This structure is composed of two lobes: the anterior or adenohypophysis and the posterior or neurohypophysis. While the posterior pituitary gland stores the hormones vasopressin and oxytocin (related to maternity and orgasm), the adenohypophysis secretes hormones that release thyrotropin, corticotropin, gonadotropins, and growth hormone.
- Related article: "Pituitary gland (hypophysis): the nexus between neurons and hormones"
Functions of this hormone
The main functions of vasopressin they are associated with their ability to regulate the activity of the kidneys; However, this hormone also has effects on other body systems, including the cardiovascular and central nervous system.
1. Retention and reabsorption of liquids
Vasopressin increases the permeability of kidney cells, increasing the amount of water they absorb; this function is called "antidiuresis" . Such a process also implies an increase in the concentration of urine due to the lower availability of fluid in the excretory system.
On the other hand, the antidiuretic hormone also reabsorbs urea, the main chemical compound in urine, formed by waste products from the body. This prevents the frequency of urination from being excessive.
2. Maintenance of homeostatic balance
Homeostasis (self-regulation of the internal environment of organisms) depends on a large number of factors; among these is the activity of vasopressin. If the homeostatic mechanisms fail, problems such as dehydration and acidosis may occur.
This hormone helps maintain the electrolyte balance of the bloodstream by retaining and resorption of adequate amounts of water, glucose and sodium , among other chemical compounds relevant to the functioning of the body.
3. Increase in blood pressure
Another of the most prominent effects of vasopressin is the increase in blood pressure. This function occurs as a consequence of the vasoconstrictive properties of this hormone, which have a moderate intensity. The enhancing role of vasopressin on hormones and neurotransmitters associated with stress It is also important to explain this effect.
4. Modulation of the stress response
Although scientific research has not confirmed it completely at the moment, there is solid evidence that vasopressin has a modulating effect on the body's response to stressful (or anxiogenic) situations.
Antidiuretic hormone regulates the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone, also called "adrenocorticotropic hormone-releasing hormone." This compound promotes secretion of corticosteroids such as aldosterone and cortisol , mainly associated with vasoconstriction and the stress response, by the adrenal gland.
5. Reduction of the sensation of pain
In recent years has begun to study the involvement of vasopressin in the modulation of pain sensations. It is believed that this hormone could act as an analgesic ; This would imply that, when released under certain conditions, vasopressin would have reinforcing effects because of the positive sensations associated with its secretion.
6. Formation of sexual and social bonds
Studies with rodents suggest that the release of vasopressin also acts as a enhancer of social ties, especially couples . In humans these effects have been found mostly in males and are related to the direct release of antidiuretic hormone in the reward circuits of the central nervous system.
- Maybe you're interested: "Love and falling in love: 7 surprising investigations"