The 5 auditory areas of the brain
People are used to living with sound. The fact of hearing everything that we have around us is something that we have so internalized that we do not even stop to think how this information enters our ears and comes to be experienced by us.
In this article we will discuss the auditory areas of the brain , which, together with the auditory system, is responsible for collecting these signals sent by the auditory nerves and sending the information already processed to the rest of the nervous system.
- Related article: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
What are the auditory areas of the brain?
The auditory pathways of our brain include both auditory pathways, which consist of bundles of fibers that carry information from the ear to the brain and vice versa, and the areas of the brain dedicated to hearing .
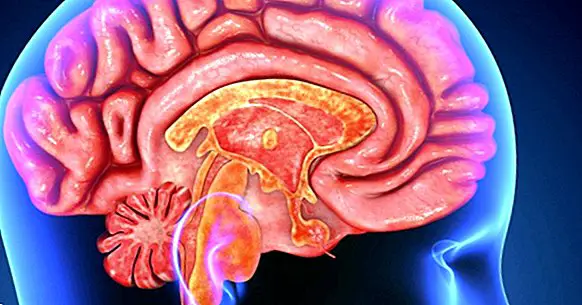
These brain areas are the brain stem together with the superior olive complex, the lemniscus and the colliculus; the thalamus and the primary auditory cortex.
In addition, it is necessary to point out the importance of the function of the auditory nerve. This nerve is essential for our hearing. Composed of more than 30,000 neurons, it is responsible, along with the auditory pathways, for transporting information to the brain by means of electrical impulses.
- Maybe you're interested: "The 10 parts of the ear and the sound reception process"
Function of the auditory pathways
Like the rest of sensory modalities, the auditory system is composed of a series of primary pathways and centers of the brain whose function is to process and transport auditory information.
In the case of the auditory pathways we find the primary auditory path whose sole purpose is to transport auditory information, and the non-primary pathway which also integrates other sensory modalities.
Primary auditory pathway
The primary auditory pathway is a short-lived neuronal circuit and with the ability to transport information very quickly, since it consists of thick myelinated fibers.
Its sole purpose is to transport the information that is collected by the cochlea, performing decoding and interpretation tasks in each of the levels. This information is transferred from one level to another until it reaches the auditory cortex.
However, before the information reaches the auditory cortex, the thalamus integrates the information and prepares to issue an answer or reaction to the auditory stimulus.
Non-primary route
After the first level, which integrates both auditory pathways as one, a part of this path known as a non-primary path deviates by joining the ascending reticular path, which integrates sensory information of all types.
The main function of this way is to gather several different sensory messages, but they are taking place at the same time, to select those that should be processed more urgently.
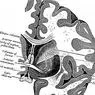
Parts of the brain stem involved in hearing
The brainstem is the structure through which almost all sensory pathways pass and its function is to communicate the spinal cord, the cerebellum and the brain. In it we can locate the nuclei corresponding to the auditory system in the brain . These are the following.
1. Cochlear nuclei
Cochlear nuclei are found on the surface of the brainstem , its main function being to examine the intensity of the sound, as well as the beginning, duration and end of it. In addition, they also provide information to the brain about the frequency of sound, that is, whether it is a bass or high-pitched sound.
2. Superior olive complex
One of the most complex systems of the auditory brain is the superior olive complex. Its dense neural network is designed to analyze and filter all acoustic information that goes to the cerebral cortex.
3. Lateral lemniscus and colliculus
The nucleus of the lateral lemniscus is involved in encoding the duration of the most complex sounds.
On the other hand, the colliculus is divided into the dorsal and external cortex and the central nucleus , which is composed of a large number of neurons.
The dorsal and external cortex is dedicated to examine the acoustic information and the recognition of complex sounds. While the central core analyzes the frequency of the sound and divides it into bass or treble.
The thalamus and the auditory cortex
Other areas of the brain involved in hearing are the thalamus and the auditory cortex. Let's see how they work.
Auditory thalamus
The auditory thalamus, also known as the Medial Geniculate Body (CGM) , receives fibers both from the dorsal and external cortex of the colliculus and from the central core of this.This part of the thalamus is divided into three specialized zones in a function. These zones are: the dorsal zone, the middle zone and the ventral zone.
Back area
The neurons of the dorsal area send projections to the secondary auditory cortex. These neurons have to respond to various different sensory stimuli.
Ventral zone
Your neurons travel to the primary auditory cortex and they also intervene in the analysis of sound frequency , maintaining the latency between communications.
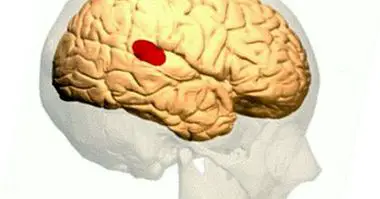
Primary auditory cortex
In people, the auditory cortex covers 8% of the entire surface of the cerebral cortex .
This primary auditory cortex consists of more than twelve different auditory fields that they are located in the upper area of the temporal lobe , where they extend by the angular turn towards Silvio's fissure; there they meet the transverse turns of Heschl.
This brain area can be divided into two differentiated regions by the organization of their neurons and by the functions of these. These areas are the following.
- The AI area is composed of neurons that determine the spatial representation of the stimulus .
- The AII area is dedicated to locate sound in outer space, to examine complex sounds and is closely related to auditory memory.
Finally, the area surrounding these two areas is responsible for analyzing and integrating the auditory information with the other sensory information that the person perceives.