Orbitofrontal cortex: parts, functions and characteristics
The human being enjoys a large amount of complex cognitive skills that allow him to adjust to a large extent to the environment in which he is located and at the moment in which he lives. He is able to plan, prepare for action, establish strategies or inhibit his own behavior. All this is very useful both in nature and in society, for example in the exchange or communication between different people and in different contexts.
It is not the same for interacting with another person in the context of a conflict or a misfortune that a party in a nightclub, to give an example, and be able to distinguish and manage the behavior to suit each situation requires of complex processes. Processes that do not appear from nothing, but that are due to the action of different brain nuclei. One of the most important in this sense and that is also key to explain much of our personality is the orbitofrontal cortex, on which this article .
- Related article: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
Orbitofrontal cortex: description and location
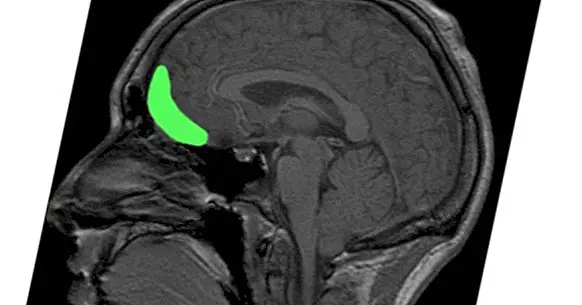
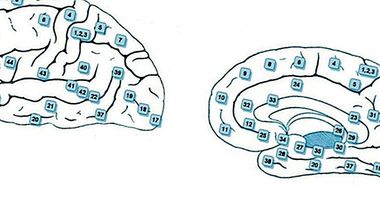
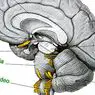
It receives the name of orbitofrontal cortex a region of the cerebral cortex which part of the prefrontal cortex and that has great importance in the regulation of social behavior, decision making and the inhibition of behaviors. This cortex is located in the frontal lobe, being in both cerebral hemispheres and being located approximately at the height of the orbits of the eyes (which is also the reason for its name).
The importance of this area is great, being involved in a lot of functions and even in the establishment of what we call personality . This is due in addition to his own performance to that we are before a part of the brain highly connected with a large number of brain regions. Among its multiple connections are those that go to the limbic system (especially the amygdala), the insula, the motor cortex, the thalamus, the hypothalamus or the hippocampus, the entorhinal cortex and most sensory areas. We are also facing one of the areas of the brain that takes longer to develop, not completing their training until adulthood.
This brain region also has some historical importance because it is the area that was injured in the first known and documented case of a subject with brain lesions in the frontal part of the brain that lived to tell about it: Phineas Gage. This young man, to whom an iron bar went through the orbitofrontal while manipulating explosives , managed to survive the injury, but later on it would begin to manifest severe alterations that would complicate its existence (hostility and aggressiveness, personality changes, inability to plan ...) until it leads to losing everything. The study of this case would allow us to begin to visualize and investigate the importance and functions of the prefrontal region of said brain region.
- You may be interested: "The curious case of Phineas Gage and the metal bar in the head"
Main functions of this brain region
We have commented previously that the orbitofrontal cortex is of great importance for the human being, being in fact fundamental for allow the adaptation of the human being to his natural and social environment as well as to carry out complex mental actions and future plans. His brain connections are many, being involved in a lot of processes. Some of the best known and explored are the following.
1. Regulation of social behavior
One of the best known functions of the orbitofrontal cortex and the one we mentioned in the introduction is to help regulate social behavior. That is, thanks to the orbitofrontal cortex we are able to adjust our actions and words to the situations, people and types of interaction that we are having at the present time. As well allows to value social norms .
2. Behavioral inhibition
Another key function in which the orbitofrontal cortex is fundamental is in the inhibition of behavior. That is, thanks to this brain region (among others) we are able to not do the first thing that comes to mind, or change our behavior as we are doing to adapt to the circumstances.
3. Involvement in personality
You can not say that the personality lies only in the prefrontal cortex, but the truth is that it has been observed that the alteration of this brain region can have serious repercussions on a person's way of being , being able to totally vary his way of behaving and reacting to stimuli.
4. Emotional management and aggression
Something in part related to the previous aspects and derived largely from their connections with the limbic system is the involvement of the orbitofrontal cortex with emotional management, especially in relation to the control of defensive and aggressive responses. It is therefore an area that allows to show alert to threat stimuli.
5. Rewards-punishment and learning systems
Studies conducted in relation to the orbitofrontal cortex have shown that this region of the prefrontal, especially with regard to its medial areas, are related to the sensitivity and learning the relationship between behavior and reinforcement . Its more lateral areas do the same with the behavior-punishment relationship. In addition, it allows the existence of sensitivity towards one or the other, something that is linked to our future choices of behavior.
- Maybe you're interested: "Reinforcement (positive and negative) in the sports field"
6. Integration of senses-experience information
Although it was already suspected that there was an involvement by the orbitofrontal cortex in this, recent research has shown that this cortex is activated and allows to integrate the current sensory information with previously accumulated information from the previous moments .
7. Analysis of decision making
Directly related to the above, it has been identified that the orbitofrontal cortex has a great implication when making decisions, given the integration of the information from the previous point and its analysis. It allows us to anticipate the choice of behavioral response that we are going to carry out , although this may vary depending on the new experiences.
8. Motivation and planning
Another area in which participation of the orbitofrontal cortex has been seen is in the ability to motivate , especially at the time of having initiative towards the behavior or maintaining it. It also influences behavior planning.
What problems can arise from your injury?
Given some of the multiple functions of this brain region and the importance of these in our day to day, it is easy to imagine the type of difficulties that can generate your injury.
It is common for lesions of the orbitofrontal cortex to derive in the appearance of aggressive behaviors, limitations in the ability to bond with others and have empathy social disengagement and disobedience of social norms, apathy, inability to generate, initiate or maintain plans and a high level of disinhibition that include difficulties to control their impulses (including addictions, sexual activity, food or aggression) and that can lead to legal issues. In fact, there is a specific syndrome that refers to the appearance of these symptoms due to brain injury: the orbitofrontal syndrome.
The injuries themselves can appear due to different types of injuries, such as for head injuries, lacerations (such as Phineas Gage), the presence of brain tumors or infections or strokes.
Bibliographic references:
- Bechara, A., Damasio, H, Damasio, A.R. (2000). Emotion, decision-making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb. Cortex, 10: 295-307.
- Kandel, E.R .; Schwartz, J.H .; Jessell, T.M. (2001). Principles of Neuroscience. Madrid: McGraw Hill.
- Nogueira, R., Abolafia, J.M., Drugowitsch, J., Balaguer-Ballester, E., Sanchez-Vives, M.V. & Moreno-Bote, R. (2017). Lateral orbitofrontal cortex anticipates choices and integrates prior with current information. Nature Communications, 8