Bupropion: uses and side effects of this drug
The snuff is one of the substances with psychoactive effects that has been consumed more legally since its discovery. Even though smoking is now prohibited in establishments and closed public spaces and its price has become more expensive based on taxes, millions of people still have the habit of smoking.
But many of these people, at some point, need to stop doing it. Although it is possible to do it based on will, in some cases they may require psychological and even pharmacological help. In this last case, one of the existing drugs used in smoking cessation is bupropion, a drug originated as an antidepressant .
- Related article: "Types of psychotropic drugs: uses and side effects"
What is bupropion?
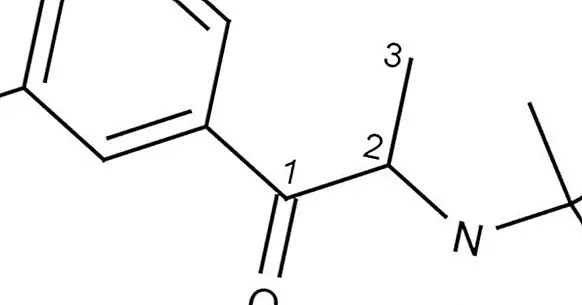
Bupropion is a well-known antidepressant-type drug, although it is more common and distinctive than its application for depression. its effectiveness in the treatment of tobacco addiction . In this sense, it is a treatment that does not include nicotine and is recommended along with some type of therapy or psychological treatment.
Bupropion is a specific inhibitor of the reuptake of dopamine and noradrenaline, or IRND , which works by increasing the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain. Compared with other drugs of the antidepressant group, bupropion has the advantage of not generating sexual dysfunctions, although on the other hand its effectiveness alone seems lower compared to other drugs on the market.
- You may be interested: "Types of antidepressants: characteristics and effects"
Mechanism of action
The functioning of bupropion and its mechanism of action is based on its role as a selective inhibitor of the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine. This implies that bupropion acts by preventing these two transmitters (associated with gratification and energy) from being recapped by the presynaptic neuron, in such a way that they are available to post-synaptic neurons for a longer time. In addition, it seems to stimulate the secretion of these neurotransmitters. Thus, the levels of dopamine and noradrenaline and their transport increase at the level of the brain, something that It can alter the mood .
Likewise, it has also been observed that it has an effect at the acetylcholine level, binding to nicotinic receptors and exerting a non-competitive antagonistic effect. Although there is no total security for this, this element is one of the possible explanations for its role in smoking cessation.
Indications: uses in disorders
Bupropion is a drug that has had various uses throughout its history. Although it was born as an antidepressant and nowadays it is still used to treat this condition both as monotherapy (single therapy) and as a combination therapy (more usual, to potentiate some specific antidepressants when the drugs of first choice are not effective), the truth is that alone It is generally considered less effective than other antidepressants .
Where this drug stands out and is most used is in smoking cessation, being effective in reducing the habit of consumption and the desire to smoke. In this sense, its mechanism of action seems to contribute to stop the craving (possibly due, on the one hand, to its antagonism of nicotinic receptors and its interaction with cerebral dopamine, although the exact mechanism is not fully known). Another disorder in which it is used is the seasonal affective disorder, in which depressive episodes appear associated with certain times of the year.
In addition to the above sometimes it has been used in the treatment of bipolar disorder , especially during the depressive episodes that can occur in this disorder (although this use requires caution since it runs the risk of turning the disorder towards a manic crisis). Also in ADHD. But in any case, more research is required and the existence of possible risks must be taken into account.
Side effects
Bupropion is a drug that is very useful in smoking cessation and is used in cases of depression, but as with other drugs its clinical usefulness is not free of risks and possible side effects .
In this sense, among the main side effects of bupropion we can find the cause of insomnia (being the most frequent), dry mouth and dizziness, headaches, nausea, constipation, tachycardia, tremors, rashes, agitation and nervousness. It can also cause a decrease in appetite.
In more severe cases, it can cause seizures (this being one of the most known serious risks), arrhythmias, hallucinations, panic or breathing difficulties or feeding or inflammation, it is necessary to go to the doctor. In some cases it can cause irritability, hostility, depression, suicidal thoughts.
Contraindications
In addition to these side effects, ** this drug is totally contraindicated in some population groups **. Should not consume this drug those people who are allergic to it or to any of its components (something otherwise obvious), those people who consume certain drugs (especially IMAOS), dependence on substances beyond the snuff (such as alcohol, drugs and drugs) and who suffer from epilepsy, brain tumors and anorexia nervosa or bulimia (since it reduces appetite).
It is also not recommended, although it can sometimes be used if the advantages are estimated to outweigh the risks, in cases of people with renal or hepatic insufficiency, head trauma, insomnia or consumption of other medications that can interact with bupropion.
Diabetics, alcoholics, hypertensives or people with psychiatric disorders (since it can contribute to the appearance of mania in bipolar or psychotic crisis in schizophrenia, among others) also have it contraindicated (or at least the treatment must be done with a high level of control of the patient's condition and the doses administered ) due to the risk of seizures and other side effects. Finally, it is also not recommended for pregnant women and infants.
References Dale, L.C .; Glover, E.D .; Sachs, D.P.L .; Schroeder, D.R .; Offord, K.P .; Croghan, I.T. & Hurt, R.D. (2001). Bupropion for smoking cessation. Chest, 119: 1357-64.