Glutamine (amino acid): characteristics and functions
Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid used by many bodybuilders for its muscle-building benefits . However, and although many do not know it, it is important for our brain and our nervous system. In this article you will find, detailed, the benefits and properties of glutamine.
- Related article: "Glutamate (neurotransmitter): definition and functions"
Glutamine: a non-essential amino acid
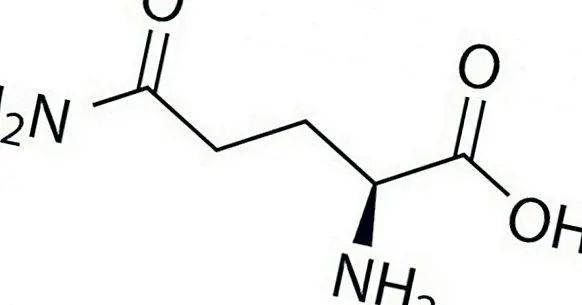
Glutamine, as mentioned in the previous paragraph, is a non-essential amino acid. And what does this mean? First, I will explain what amino acids are and then the difference between essential and non-essential amino acids
What are non-essential amino acids
Amino acids are essential nutrients for our body , because they are the raw material of the proteins. In nature there are hundreds of them, but only 20 are part of proteins (protein amino acids). The difference is that some of them synthesize the body and others do not, so it is necessary to get them through the diet. The former are called non-essential amino acids, while the latter are the essential amino acids.
- You can deepen this topic in our article: "The 20 types of proteins and their functions in the body"
Therefore, glutamine belongs to the first group, and is found in large quantities in both blood and muscle, although it is a non-essential amino acid, that does not mean that it is not important, because participates in the construction of strong muscles, as well as in the maintenance of a healthy and productive brain .
Glutamine in the brain
In recent decades, glutamine has been gaining ground in the world of sports nutrition for its benefits for the increase of muscle mass. But nevertheless, the brain also benefits enormously from this substance for various reasons .
Glutamine is key in the increase of brain function because it participates in the increase of two very important neurotransmitters: glutamate and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, for its acronym in English), two chemicals used by neurons of the nervous system to time to communicate with each other.
The relationship between glutamine, glutamate and GABA
From glutamate the body forms glutamine, which in turn produces glutamate, the main excitatory neurotransmitter of the nervous system. Glutamate deficiency is associated with fatigue or performance problems . Therefore, glutamine participates in the improvement of attention, learning and increases cognitive function.
But glutamine also increases the production of GABA and vice versa. GABA is the most important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Low levels of this neurotransmitter are associated with anxiety disorders, sleep problems, depression and schizophrenia.
Implications of glutamine
Thus, glutamine performs different functions within the human brain and is involved in changes in mood, anxiety, irritability or insomnia. Also, this substance increases short and long term memory and increases concentration; and the glutamine deficit is associated with:
- Concentration problems
- Decrease in sexual appetite
- Mental fatigue
- Increased cravings for sugars and fats
- Less alert feeling
Glutamine and its relationship with stress
The demand of glutamine by the body increases in times of physical and mental stress weakening the body. And, at the same time, Glutamine is an important supplier of energy to the immune system and the cells of the intestine or, what creates a vicious circle. In these moments of physical and mental stress, the intake of glutamine supplements is highly recommended, always after consulting with the family doctor.
For those who are reluctant to take supplements, it is possible to get glutamine through food intake. But although we can find this substance in some foods, glutamine is usually destroyed after the cooking process. Therefore, it is advisable to consume these raw products. Among the foods rich in glutamine include: spinach, parsley, milk or nuts.
Glutamine and muscle benefit
Glutamine is the most frequent amino acid found in muscles, since, in skeletal muscle, it represents approximately 60% of its constituent amino acids. It consists of 19% nitrogen, which turns glutamine into a primary transporter of this chemical to the cells.
During intense training, glutamine levels drop drastically , causing a decrease in strength, endurance and recovery.In fact, it can take up to 6 days for the body to return to normal levels; that is why glutamine, especially for athletes, plays an important role in the synthesis of proteins. Several investigations have concluded that supplements can minimize this wear and tear and improve protein metabolism.
Mainly, at the muscular level, glutamine provides the following benefits:
- Involved in protein synthesis and prevents muscle catabolism
- Promotes muscle recovery
- Stimulates growth hormone
- It favors the recovery of glycogen