Putamen: structure, functions and related disorders
The basal ganglia are a subcortical region that intervenes in diverse physical and cognitive functions, particularly in the movement, both voluntary and automatic. The nuclei that make up this superstructure have been grouped in different ways, giving rise to denominations that overlap each other.
The putamen is one of the sections of the basal ganglia . In this article, we will describe the structure, functions and disorders associated with putamen injuries, paying particular attention to the relationship of this nucleus with the rest of the basal ganglia regions.
- Related article: "Basal ganglia: anatomy and functions"
What is the putamen?
The putamen is a cerebral structure that has a fundamental role in the preparation and execution of limb movements . It is part of the anatomical-functional region known as "basal ganglia", which regulates voluntary motor skills, automatic habits and procedural learning.
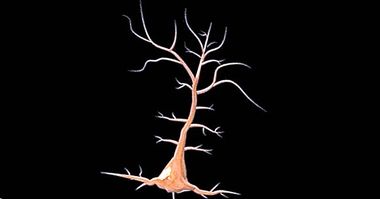
It is constituted by gray matter, that is, by neuron bodies, unmyelinated dendrites and glial cells. It is located below the cerebral hemispheres, at the base of the telencephalon and in the central part of the brain. Its shape is approximately circular.
The functions of the putamen depend on the neurotransmitters GABA and acetylcholine , as well as enkephalin, an opioid peptide involved in the perception of pain and its regulation. On the other hand, gamma-aminobutyric acid or GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, while acetylcholine (ACh) activates the movement of muscles.
- Maybe you're interested: "GABA (neurotransmitter): what it is and what role it plays in the brain"
Structure and anatomy
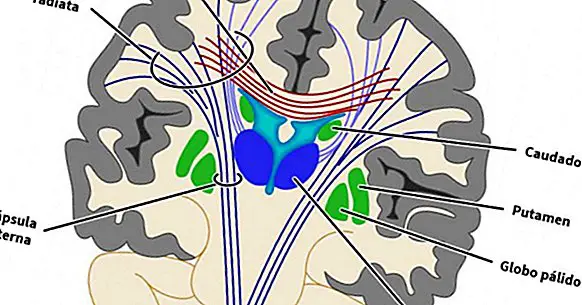
The putamen, the striate body, the pale globe, the caudate nucleus, the nucleus accumbens, the subthalamic nucleus, the substantia nigra and the red substance form the basal ganglia. The putamen is the outermost of these nuclei .
The word "ganglion" is usually used to designate clusters of neuronal cells that are located in the peripheral nervous system, so the nomenclature is paradoxical in this case, when the basal ganglia are located in the brain.
Morphologically and functionally the putamen is intimately related to the caudate nucleus, the pale globe and the nucleus accumbens ; As a whole, these three structures are known as corpus striatum. Also, we call "lenticular nucleus" the union between the putamen and the pale globe.
The putamen is connected to the black substance and the pale balloon by different nerve pathways. This allows the exchange of information between the basal ganglia and the cerebral cortex, with the thalamus fulfilling its usual function as a relay nucleus.
- Related article: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
Putamen functions
The two main functions of the putamen are the regulation of movement and the facilitation of different types of learning . He is also involved in disgust and in the feeling of hatred.
Let's see what are the ways and mechanisms that allow the putamen to fulfill these functions.
1. Movement regulation
The putamen and the rest of the structures that make up the striatum send afferences to the brainstem, to the thalamus regions involved in the movement and the motor cortex. These signals ensure that locomotion occurs properly.
Other motor activities related to the putamen are the selection of movements, regulation of motor learning and planning of motor sequences. It is considered that this structure is important especially for the control of the arms and legs.
However, a motor function is not specifically attributed to the putamen, but this role is due to its connections with other structures, both cortical and subcortical.
2. Operant conditioning
Operative or instrumental conditioning is a type of learning that is based on the positive (reinforcement) or negative (punishment) consequences of the behavior. The dopaminergic and cholinergic neurons that abound in the basal ganglia have a key role in this regard.
3. Implicit learning
Implicit learning is that which occurs passively, through mere exposure to certain stimuli. It is believed that dopamine and acetylcholine explain this function of putamen, as happens with operant conditioning.
4. Category learning
Scientific research suggests that putamen also influences the learning of categories, that is, the broad psychological constructs which encompass more specific ones.For example, the category "animal" includes the concepts "elephant", "fish" and "fox".
- Related article: "The 8 superior psychological processes"
5. Disgust, contempt and hatred
It has been theorized that the putamen is involved in feelings of disgust and contempt due to their connections with the insula; this way is known as "hate circuit" . It is also believed that the putamen is also part of the motor system that acts as a consequence of these emotions.
Related disorders
Injuries in the putamen cause involuntary movements such as tremors, sudden spasms or choreas (Rapid shaking of the feet and hands). This type of motor symptoms are very characteristic of the damage in the basal ganglia, as well as in the cerebellum, which is functionally related to these nuclei.
Several neurodegenerative diseases cause motor symptoms of this type because they destroy tissues of the putamen and other basal ganglia. Particularly noteworthy are Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease and dementia of Lewy bodies.
Other psychological and neurological disorders What are related to putamen are attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, Tourette syndrome, schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder and some types of depression.
Likewise the damage in this structure can cause the restless legs syndrome , a disorder characterized by a sensation of discomfort in the lower extremities. When moving them the discomfort is reduced, reason why the people with this alteration are impelled to shake them. The symptoms appear in a resting state, making it difficult to reconcile sleep.