Brain ischemia: symptoms, causes and treatment
One of the most feared phenomena and brain problems worldwide is the appearance of a stroke or stroke, which is one of the most frequent causes of death worldwide.
The reason is the fact that their presence generates the death of part of the cells of the brain, something that can generate different consequences more or less disabling and compromise survival depending on the areas that are damaged.
But the truth is that when we talk about stroke we are really talking about two major types of stroke: we can be faced with cerebral hemorrhage or cerebral ischemia .
It is on this last type that we are going to focus on throughout this article, in order to discuss what it is, for what reasons it can happen and what kind of intervention can be carried out in those who have suffered it.
- Related article: "The 12 most important brain diseases"
What is a cerebral ischemia?
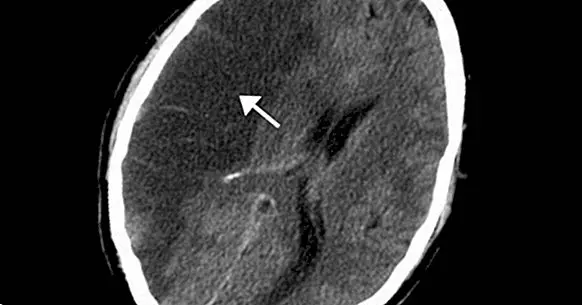
It is called cerebral ischemia to one of the great types of stroke that exist, which is characterized by the appearance of a degeneration or neuronal death in the brain derived from the existence of some type of blockage in any of the blood vessels that supply the brain .
This blockage causes the blood to not reach the nerve cells that the blood vessel should irrigate, so that by not receiving a sufficient level of oxygen and nutrients the affected cells degenerate and die quickly. Thus, technically we speak of ischemia when for some reason the supply of nutrients and oxygen that the brain cells need to survive is interrupted.
- You may be interested: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
symptom
Brain ischemia is an alteration that can generate a great variety and diversity of symptoms , since the obstruction can occur in any of the blood vessels that irrigate any area of the brain. Thus, the specific symptoms will depend to a large extent on the affected area.
However, there are some symptoms that are common in both ischemia and other cerebrovascular accidents: the sudden onset of paralysis or numbness of a part of the face or half of the body, sudden changes in speech (including aphasias in which you lose the ability to understand and / or produce speech) and the sudden hypotonia or lack of muscle tone in a part of the body.
In addition, other types of alterations may arise, such as dizziness, headaches, hallucinations, personality changes, tremors and / or seizures , blurred vision or loss of specific sensory abilities.
Between ischemia and cerebral hemorrhage ischemia is much more common, there are a lot of factors and situations in which a blockage of cerebral vessels can appear.
Its main types
Within the ischemias we can also find different types, depending on how and why the block in question appears and even to what extent it affects more or less brain regions. Among the different types, the following stand out.
1. Thrombotic ischemia
This type of ischemia occurs when inside the blood vessels of the brain there is an obstruction that prevents the passage of blood . This obstruction is called a thrombus, and usually comes from the presence of cholesterol plaques in the vein or artery or from the existence of a clot that forms within the cerebrovascular system itself.
2. Embolic ischemia
Embolic ischaemia or embolism differs from the previous one because the element that causes the blockage of the cerebral blood vessel, in this case called the embolus, arises in some part of the organism different from the brain and travels along with the bloodstream throughout the body until that eventually reaches the cerebrovascular system, causing at some point a tamponade if it encounters a smaller vessel than him. It is what can happen for example with some blood clots .
3. Transient ischemic accident
Transient ischemic attack is a type of cerebral ischemia in which, as in the rest, some element that blocks brain vessels suddenly appears, but nevertheless the proper functioning of the organism manages to unblock it by itself quickly (for example because the blood flow manages to push or fragment the embolus or thrombus).
In these cases the symptoms usually have a short duration and the subject can fully recover, although the fact that it has appeared means that the subject is at risk of more severe ones appearing.
4. Lacunar stroke
It is understood as such a type of cerebral ischemia in which the affected blood vessel is an arteriole, ie one of the small branches of the arteries that enter the depths of the different areas of the brain .
That ischemia occurs at this level implies that the affected areas will generally be small and their effects smaller than in other types of stroke, but can also have serious repercussions and even cause death depending on the region where it occurs.
- Related article: "Lacunar infarction: causes, symptoms and treatment"
5. Focal cerebral ischemia
It is called as such a type of ischemia in which the interruption of blood flow occurs in a blood vessel that will irrigate a specific brain area , so that the effect at the neuronal level is specific to the specific area that is damaged or dies.
6. Global cerebral ischemia
In this case, ischemia does not occur in a specific vessel but occurs at a more globalized level, being all or almost all the brain that does not receive enough oxygen or nutrients. In this case the problem is global and has the potential to generate many more repercussions on the subject who suffers.
7. Hemodynamic ischemia
In this little-known type of ischemia there is no blockade as such, but an interruption of the arrival of oxygen or nutrients to the brain . The cause of this type of stroke is the absence of a deficit in the blood pressure level that leads the blood to circulate at the speed necessary to nourish the cells.
Causes
Technically, the presence of ischemia implies the existence of some type of blockage or difficulty in the arrival of blood with oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the brain. In this sense, the most common causes are usually blood clots or cholesterol plates and lipids that clog the arteries . But beyond that there are many possible causes that can lead to this type of stroke.
Among the numerous risk factors for its appearance we find the presence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cholesterol, previous brain lesions (for example due to scarring of some vascular lesion), heart problems (as in the case of cerebral ischemia hemodynamics), malformations, traumatisms (which can generate blood clots), lack of sufficient nutrients, tumors, smoking or consumption of certain drugs .
Affectation in the life of the subject
The suffering of a cerebral ischemia usually supposes a great affectation in the life of the patient, which can suffer important sequelae during a time or even during all his life.
At a direct level, the patient may suffer from a great diversity of problems derived from the death of their tissues, which can range from aphasia to paralysis of part of the body, including tingling, cognitive difficulties (such as concentration, etc.). or memory), sensory deficits, sleep problems, movement, sexuality or nutrition. And unfortunately, these problems are not always going to be solved or compensated, something that can lead to the patient having different degrees of disability .
It must also be borne in mind that at the social and occupational level, the consequences of ischemia can have consequences: for example, if the patient suffers from an ischemia-related aphasia, he will find it difficult to communicate effectively, something that can be very frustrating for the subject and generate misunderstandings with the environment.
Finally and beyond the direct consequences of ischemia, we can not ignore the great emotional impact of suffering this type of disorder . The subject has experienced a situation of great risk for his life and it is not uncommon for anxiety or depressive problems to appear, as well as a great fear of the possibility that it may happen again.
Treatment
In cases of cerebral ischemia, the rush to go to the medical center is fundamental and can save the life of the sufferer, as well as reduce the possible effects of cell destruction .
Once the problem is identified, at a medical level it is possible to inject substances that allow the dissolution of clots or even use surgery to remove the clot (being able to reach the cerebral arteries with procedures such as angioplasty from other parts of the body).
Once the problem has been treated and the blood supply returned to normal, and after a period in which the patient is under observation and in which it is possible to reduce part of the area affected by the lack of risk (the so-called ischemic penumbra in which a brain area has been partially affected but it has not completely died, and in some cases it can partially or completely recover functionality), it will be necessary to assess the neuropsychological status of the patient .
For this purpose, it will be necessary to evaluate its functionality in the different areas, both at motor and cognitive level, in order to identify the possible deficits and alterations caused by the death of nerve cells. Once this has been done, it will be necessary to elaborate an individualized treatment, in which, depending on the case, it may be necessary to use occupational therapy, cognitive stimulation (in which aspects such as memory, executive functions or attention can be worked on), speech therapy and / or physiotherapy.
It is about performing a neuropsychological rehabilitation of the patient, favoring recovery or compensation of the affected functions.
It can also be useful psychological therapy to the affected, since the sequelae of ischemia can be experienced with panic and suffering and cause (either directly as a result of ischemia or indirectly deriving from the perception of deficits) emotional disturbances, anxiety, cognitive distortions and problems of psychosocial adjustment.
Bibliographic references:
- Kuźma, Elżbieta; Lourida, Ilianna; Moore, Sarah F .; Levine, Deborah A .; Ukoumunne, Obioha C .; Llewellyn, David J. (2018-08). "Stroke and dementia risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Alzheimer's & Dementia. 0 (0)
- Lewis. S.L (2008). Medical-Surgical Nursing. Vascular disorder