Epithalamus: parts and functions of this brain structure
The human brain is not an amorphous and homogeneous mass , but it can be found in a large number of structures and substructures with large differences between them, which work with different neurotransmitters and have various functions.
Although some of these structures of the brain are known by many people, such as the amygdala or the hippocampus, others are more unknown despite having an important role in regulating our behavior. For example, helping to regulate hormones and to follow circadian rhythms. This is the case of the epithalamus , which we are going to talk about in this article.
- Related article: "Parts of the human brain (and functions)"
What is the epithalamus?
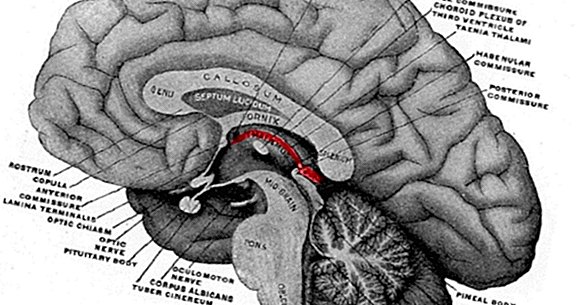
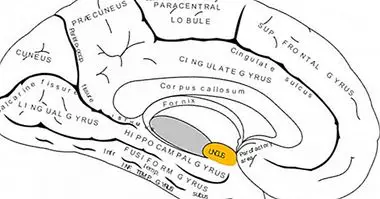
The epithalamus is a relatively small structure that is part of the diencephalon and that can be found just above the thalamus and touching the roof of the third ventricle. It is a structure mainly linked to the limbic system, being relevant in the management of instinct and emotions.
It is also associated with the neuroendocrine system through the pineal gland, one of the main structures that forms part of the epithalamus that is also part of this system. We are dealing with a structure with a wide gamma of connections with the rest of the brain regions, including the olfactory system (also related to the perception and reaction to odors) and many other structures of the encephalon.
- Related article: "What is the thalamus and what is its function in our nervous system?"
Parts of the epitalamo
The epithalamus is configured by a set of structures of great importance for the human being. Apart from the medullary striae, nerve fibers that establish connections with other regions of the brain, we can find two large structures, which are the most relevant and known of the epitalamo.
Epiphysis or pineal gland
The most known structure of the epithalamus is the pineal gland. It is an element known since antiquity (specifically the first information that has been found about it date from the third century BC), proposing Descartes the existence in it of animal spirits related to emotions.
Inervated by the autonomic nervous system and being connected to other nuclei such as the septals, the pineal gland is an important regulating brain structure of the neuroendocrine system , participating in functions such as the regulation of energy and sexuality.
One of the most important aspects of the pineal gland is the fact that it is responsible for secreting melatonin from serotonin, when the illumination is nonexistent or very low. In this way the epiphysis is essential in regulation of circadian rhythms and sleep and wakefulness .
It is also involved in the synthesis of endorphins and sex hormones such as luteinizing hormone, as well as sexual growth and maturation (which delays its activity).
- Related article: "Pineal gland (or epiphysis): functions and anatomy"
Habenula or habenular nuclei
In addition to the pineal gland, the other major structure of the epithalamus is the habenula or habenular nuclei (since there are actually two structures). It is linked to the previous one, and it is very important when receiving and send connections nuclei of the limbic system and reticular formation . Habenular nuclei are elements that, unlike epiphyses, do not have endocrine functions.
Acts largely as a bridge between various brain areas (including in addition to the above the thalamic nuclei, those of the forebrain or preoptic area) but precisely because of these connections also seems to be involved in the motivation not to act, fear and negative evaluations of the facts similar to those that in the past could have caused us harm. Finally, they are also linked to the ability to provide emotional information to the smells .
Its functions
As we have indicated previously, although the epithalamus is not especially known, its existence and functioning in the brain is of great relevance for the human being, having important functions for our adaptation and survival.
As part of the limbic system, participates in the management of emotion and motivation . In this sense, its role in different disorders such as depression or anticipatory anxiety can be explored.
One of these functions is the management of circadian rhythms, our biological clock that regulates at what times of the day we have and use more or less energy.In this sense it also has great importance in the management of sleep, because the pineal gland present in the epitalamo reacts to the absence of light producing melatonin and decreasing energy levels, facilitating sleep.
It also participates in sexual growth and maturation , adjusting the biological rhythm in which we develop and we become adults. Finally, their connections with olfactory pathways make them relate to the ability to perceive smells and give them an emotional meaning.
Bibliographic references
- Kandel, E.R .; Schwartz, J.H. & Jessell, T.M. (2001). Principles of neuroscience. Fourth edition. McGraw-Hill Interamericana. Madrid.