Gray matter of the brain: structure and functions
Almost everyone has ever heard about the gray matter that one or another person has. In Spain it is a concept that has been popularly associated with intelligence, but in reality its role is much more important than that.
Gray matter can be found in the brain, yes , and also its existence has to do with the way in which the mental processes related to, among other things, cognition and intelligence are developed. But having more or less amount of gray matter does not imply being more or less intelligent. This is because its function is more general and essential, and has to do with the basic functioning of the nervous system.
What is gray matter?
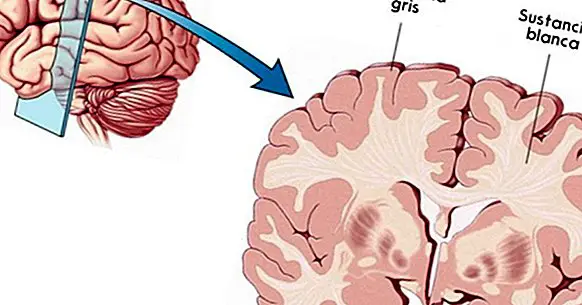
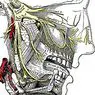
Gray matter, also called gray matter, it includes the zones of the central nervous system in which the somas of the neurons predominate (that is, the part of the neuron in which its nucleus is located and its "body" from which the branches depart).
The gray color of these areas is opposed to the target of the rest of the nervous system, which has that aspect because in them the axons of the neurons predominate, that is to say, the prolongations that are born from the somas and that are covered by myelin, of white color .
In qualitative terms, there are no relevant differences between the composition of the white matter and that of the gray matter: in both there are neuronal soma, dendrites and axons with myelin. However, yes there are significant differences in the quantities and proportions in which these elements are present in each of them .
So, technically, gray matter is not a part of the brain, but the material with which some parts of the brain are constructed.
The distribution of gray matter
The areas of the brain and spinal cord that are formed by gray matter do not form a homogeneous group, but are distributed and in some cases there is white matter between them. However, in most cases these areas are large enough to be easily seen by the naked eye.
In the medulla, the gray matter is in the central and lateral part (in any of its sections, regardless of the height at which it is), but in the brain is more distributed.
The cerebral cortex, for example, consists of gray matter , but the same happens with the basal ganglia, which are located below, with the deepest and most superficial part of the cerebellum and with many other scattered areas, such as the thalamus and the hypothalamus.
The function of these areas
Unlike what white matter does, in which myelin causes nerve impulses to be transmitted rapidly by axons, gray matter can not make the information flowing through it go so fast. The main function of these zones is not to make electricity pass quickly through them , but it has to do with the processing of information, whatever the type.
As the content of the information processed by gray matter areas is very diverse, the effects of a decrease or an increase of this substance are also varied. That is why injuries in these areas depend on the type of structure they affect. However, no part of gray matter can work without the help of white matter, since they need to be connected to each other in order to function correctly.
As for the gray matter of the spinal cord, it is in charge of acting as an information directory , that is, where it is decided what information goes in and out to the nerves of the peripheral nervous system and what information should travel up or down the spinal cord. In addition, there are some theories about memory according to which memories are stored chemically within neuronal cells, much more abundant in this type of brain tissue.
Concluding
The presence of gray matter indicates that the part of the brain in which it is found receives information from many areas of white matter and that, in some way, they function as information processing clusters and in which the nerve impulses that travel through the axons meet with a relay that directs them to another destination.
This implies, among other things, that gray matter and white matter are needed to work as they should; not in vain are two types of brain tissue differentiated by the concentration of the part of the neurons that predominate most in them (axons or somas), and these small nerve cells form an organic unit that can not be separated without destroying it.