Triglycerides: what they are and how they affect our health
Among the various substances that constantly travel through our blood are the lipids, molecules with very important functions for living organisms. The most common type of these molecules are triglycerides .
At adequate levels, the latter can keep our body in balance, but otherwise, triglycerides can cause serious health risks. For this reason they are one of the most medically controlled molecules.
In this article we will see what triglycerides are, what their function and risks are for the organism and how we can maintain their levels in balance.
- Related article: "Types of fats (good and bad) and their functions"
What are triglycerides and what function do they have?
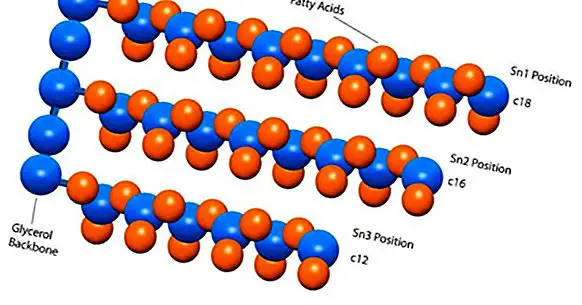
Triglycerides are the most common type of lipid in our bloodstream. As such, it is about sets of molecules composed mainly of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen . They are, likewise, molecules insoluble in water and found in different living beings, fulfilling different functions according to the specific type of lipid in question.
For example, lipids such as steroid hormones can be used to regulate the functioning of specific cells. Another type of lipid, which we know as structural function lipids, can be used to shape cell membranes. Likewise, the type of lipids that we know as triglycerides can serve to generate the reserves of energy necessary for our daily activity.
For absorption, transport and metabolism from the latter, organs such as the small intestine and the liver participate; anatomical structures such as the lymphatic system; and molecules such as lipoproteins.
How do we get them?
As with other nutrients, triglycerides reach our body through food and substances that we consume daily. The substances that most frequently give us triglycerides are butter and oils , although they are also generated from the consumption of calories that come from different foods.
According to its components, and the frequency or quantity in which they are consumed, some foods and substances favor the process of absorption of lipids. However, there are others that can hinder this process, causing its accumulation.
Specifically, when we consume calories that our body does not need immediately (additional calories), the latter are converted into triglycerides and are deposited in different cells and tissues. When it occurs moderately, this process has the objective of maintain our body with the necessary reserves of energy For the day to day.
That is, when we have an activity that requires high levels of energy, cells that contain triglycerides are released and travel to different tissues, to nourish them and keep them active. However, when triglycerides accumulate excessively and unnecessarily, they can cause serious health problems.
- Maybe you're interested: "Psychology and Nutrition: the importance of emotional feeding"
Normal level and high level
As we see, triglycerides have both a function and an important risk in our body. Your concentration levels they are measured by a test that also allows us to know cholesterol levels . In your case, triglycerides are measured in milligrams per deciliter (abbreviated as follows: mg / dL).
The triglyceride levels measured from Normal to Very High for the adult are as follows:
- Normal: less than 150 mg / dL.
- High limit: 150 to 199 mg / dL.
- High: 200 to 499 mg / dL.
- Very high: from 500 mg / dL.
These levels can be detected through an analysis that consists of extracting blood from the vein that is in the inner part of the elbow. The blood can also be extracted from the back of the hands. In any case, the test is done after 12 hours of fasting.
Consequences of high triglyceride levels
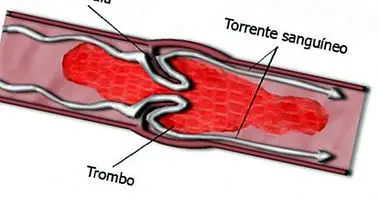
From a high limit of triglyceride concentration increase the risks of developing a heart disease and / or a metabolic syndrome ; which is when the same person presents the set of cardiovascular disease risk factors: central obesity, diabetes, high triglycerides and low lipoprotein levels and low density, and high blood pressure.
In addition, if triglyceride levels increase to 150 mg / dL or higher, these levels are considered hypertriglyceridemia. As the name implies, it is the very high concentration of triglycerides in the blood. The presence of hypertriglyceridemia indicates that the risk of developing coronary heart disease has increased, although it is also a risk factor for acute pancreatitis if it occurs at even higher levels (when it reaches 1000 mg / dL or more).
Likewise, hypertriglyceridemia has been associated with the development of arteriosclerosis; both by the levels of triglycerides and by the cholesterol content of the remaining lipoproteins (protein and lipid groups that carry fat through the body, and that being remnants, it is the lipoproteins converted into fatty acids and accumulated throughout of the day).
In this sense, although hypertriglyceridemia refers only to the increase of triglycerides, in some cases it may be related to hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol levels), which may indicate a high risk of suffering from different types of cardiovascular disease, as ischemic heart disease and myocardial infarction .
Causes and treatment of high triglycerides
The main cause of high triglyceride levels is the intake of more calories than we can burn. This amount is caused mainly by the excessive consumption of sugar and saturated fats. Likewise, some lifestyles, such as smoking or consuming alcohol frequently, are two risk factors for high triglyceride levels .
On the other hand, some medical conditions that can generate high triglycerides are the following:
- Overweight and obesity .
- Diseases of the thyroid.
- Type 2 diabetes.
- Kidney or liver diseases .
- Genetic conditions, such as combined familial hyperlipidemia.
- Alterations in the activity of lipoproteins (those that regulate the metabolism of lipids in the body).
In this sense, the prevention and treatment of high triglyceride levels consists of prevent lipids from accumulating in our blood and tissues , by preventing the risk factors mentioned above.
One of the most important treatments is to make changes in lifestyles. For example, it is essential to maintain control of our weight through regular physical activity combined with a balanced diet. Specifically, it is important to limit the consumption of added sugars, saturated fats, and flours or refined foods, as well as alcoholic beverages, since all this produces additional calories that are converted into triglycerides, and often accumulate excessively within our organism. Instead of saturated fats, easily absorbed fats derived from olive oil or fish can be used .
Likewise, and in the event that high levels of triglycerides require medical treatment for their reduction, it is common to prescribe drugs that are also used to treat cholesterol. Among these are nicotinic acid, fibrates and inhibitors of cholesterol absorption.
Bibliographic references:
- MedlinePlus (2018). Triglycerides. MedlinePlus Retrieved August 20, 2018. Available at //medlineplus.gov/spanish/triglycerides.html.
- Texas Heart Institute (2018). Metabolic syndrome. Texas Heart Institute. Retrieved August 20, 2018. Available at //www.texasheart.org/heart-health/heart-information-center/topics/sindrome-metabolico/.
- González-Chávez-A., Simental-Mendía, L.E. and Elizondo-Argueta, S. (2011). Triglycerides / high HDL-cholesterol ratio and insulin resistance. Surgery and surgeons, 79: 126-131.
- Nordestgaard, B., Benn, M., Schnohr, P., et al. (2007). Nonfasting triglycerides and risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. JAMA, 298 (3): 299-308.
- Gan, Sl., Edwards, AL., Symonds, C.J., et al. (2006). Hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis: A case-based review. World, J. Gastroenterology, 12 (44): 7197-7202.